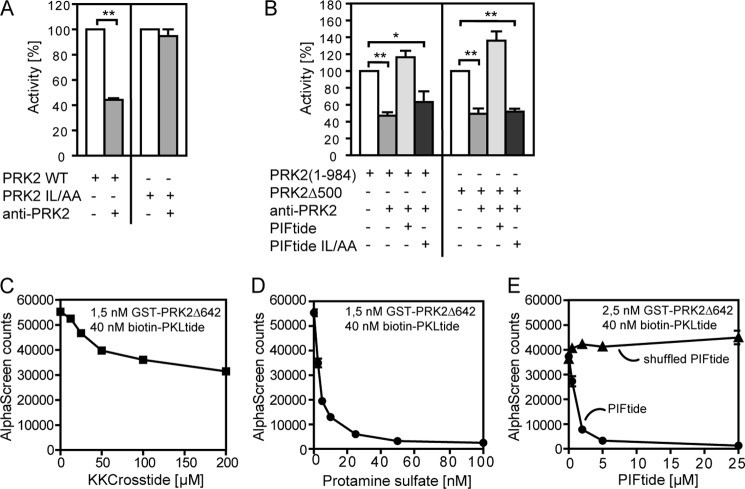
FIGURE 6.
The communication between N-terminal and C-terminal regions of PRK2. A and B, the kinase activity of GST-PRK2 proteins purified from HEK 293 cells was measured in vitro using the polypeptide KKCrosstide as a substrate in the presence or absence of the PRK2 C-18 antibody directed to the C terminus of PRK2. A, effect of the PRK2 C-18 antibody on the kinase activity of PRK2 WT and PRK2 with alanine substitutions of Ile965 and Leu966 (PRK2 IL/AA). B, the addition of PIFtide (amino acids 961–984 of PRK2, REPRILSEEEQEMFRDFDYIADWC) but not PIFtide IL/AA abolished the inhibition of the kinase activity of PRK2(1–984) (left) and PRK2Δ500 (right) mediated by the 2 (PRK2 C-18) antibody. C–E, analysis of the effect of the substrate peptide KKCrosstide (C), protamine sulfate (D), PIFtide and Shuffled PIFtide (DFIREESAWQDRSEFLMDEPYERI) (E) on the interaction between GST-PRK2Δ642 and biotin-PKLtide using AlphaScreen technology. Similar to Shuffled PIFtide, a PIFtide mutant (REPRAASGGGQEMRRDRAYIADWS) also did not affect the binding of GST-PRK2Δ642 and biotin-PKLtide (data not shown).