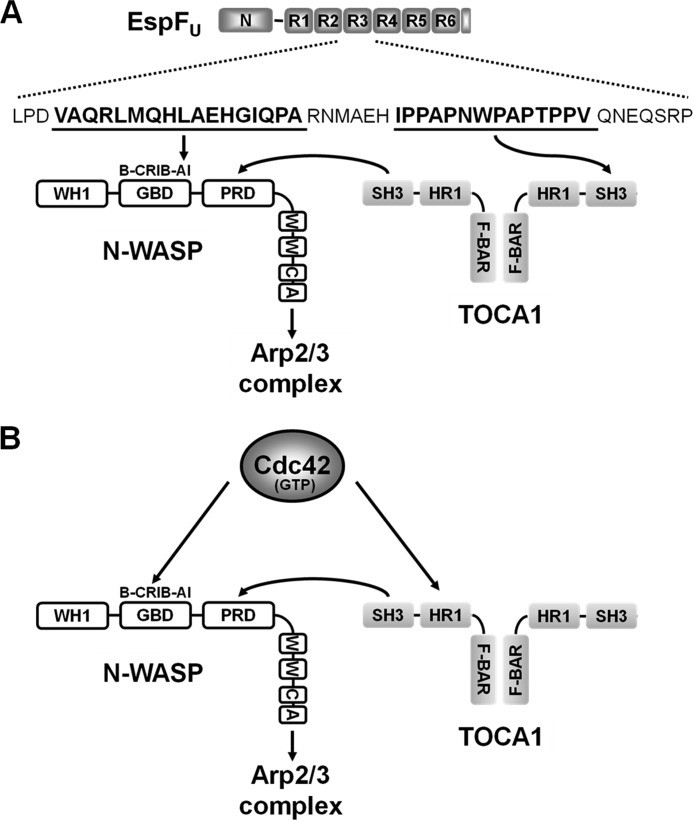
FIGURE 9.
Model for EspFU-mediated recruitment of TOCA1 and enhancement of N-WASP activation. A, EspFU contains an N-terminal sequence (N) important for entry into mammalian cells and multiple 47-residue peptide repeats (R1-R6) that include an N-WASP-binding amphipathic helix and a proline-rich SH3-binding sequence. Interactions between an EspFU repeat and the N-WASP autoinhibitory (AI) motif within the GBD exposes the WCA region to promote Arp2/3 complex activation. The EspFU repeats also bind to the SH3 domain of TOCA1. In a simple model, one subunit of a TOCA1 homodimer may interact with EspFU, while the SH3 domain of the other subunit may enhance N-WASP activation by binding to the N-WASP proline-rich domain (PRD). Other N-WASP sequences include a WASP-homology-1 (WH1) domain, a basic (B) peptide, and a C-terminal WCA region. B, in contrast to EspFU, Cdc42 binds to the N-WASP Cdc42/Rac-interactive-binding (CRIB) motif within the GBD and the TOCA1 HR1 domain to promote actin assembly. The TOCA1 SH3 domain can facilitate N-WASP activation by binding to the PRD.