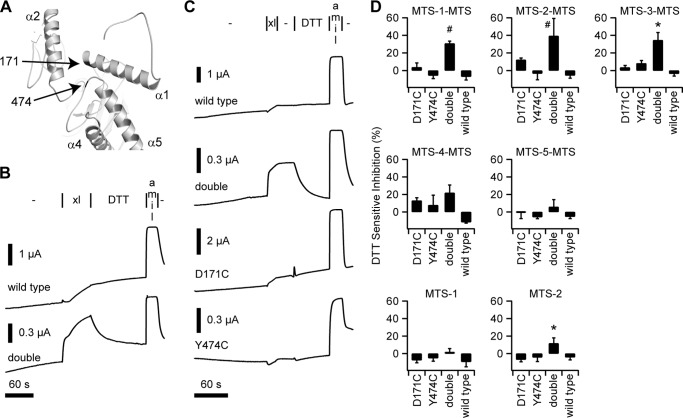
FIGURE 3.
Conformational trapping using sites in the finger and thumb domains. A, model of the α subunit finger domain highlighting interfacing residues 171 and 474 in the finger and thumb, respectively. B, preliminary experiments with MTS-2-MTS (xl) show the effect of a 1-min addition of the reagent, followed by a 2-min wash with DTT to wild type and αD171C,Y474C (double) channels. C, representative recordings of the effect of adding MTS-2-MTS (xl) for 15 s, followed by a 30-s wash (−), and then a 1-min wash with DTT. Amiloride (amil) was added at the end of each experiment to measure the background current in each experiment. D, DTT-sensitive component of inhibition by various MTS compounds of wild type ENaC, each of the single mutants (D171C and Y474C) and the double mutant. DTT-sensitive inhibition was calculated by dividing the change in current upon DTT addition by the total amiloride-sensitive current. Values are mean ± S.D. (n = 5–10). *, p < 0.01 versus wild type and single mutants using the same MTS reagent, as determined by ANOVA and a Newman-Keuls post hoc test. #, p < 0.01 versus wild type and single mutants using the same MTS reagent and all channels using the analogous monofunctional MTS reagent, as determined by ANOVA and a Newman-Keuls post hoc test.