Figure 1.
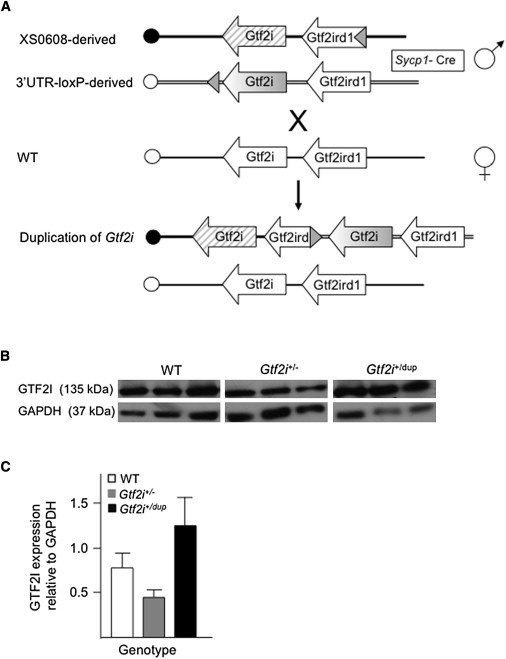
Generation of Mice with Decreased or Increased Gtf2i Dosage
(A) Schematic representation of the generation of mice with duplication of Gtf2i. XS0608 contains a loxP site inserted into intron 4 of Gtf2ird1, whereas the 3′UTR-loxP line contains a loxP site downstream of the last coding exon of Gtf2i. Recombination between the loxP sites in vivo resulted in duplication of the entire Gtf2i gene in the male gamete of transloxer male mice carrying both loxP sites in trans, as well as a Cre transgene under the control of the Sycp1 promoter. Duplicated chromosomes were transmitted to offspring upon crossing with wild-type (WT) females. The centromere of mouse chromosome 5 is represented by the circle at the left end of each diagram. LoxP sites are represented by a shaded triangle.
(B) Immunoblot analysis of GTF2I from whole brain of P8 mice with the use of a polyclonal antibody (610943, BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ). GAPDH (ab36840, Abcam, Cambridge, MA) was used as a control for protein loading (50 μg per lane). Representative blots from three independent pups are shown.
(C) A graph (created with Image J [National Institutes of Health]) comparing the densitometric measurement of GAPDH with that of GTF2I in whole brain of P8 mice. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (n = 3 for each group).
