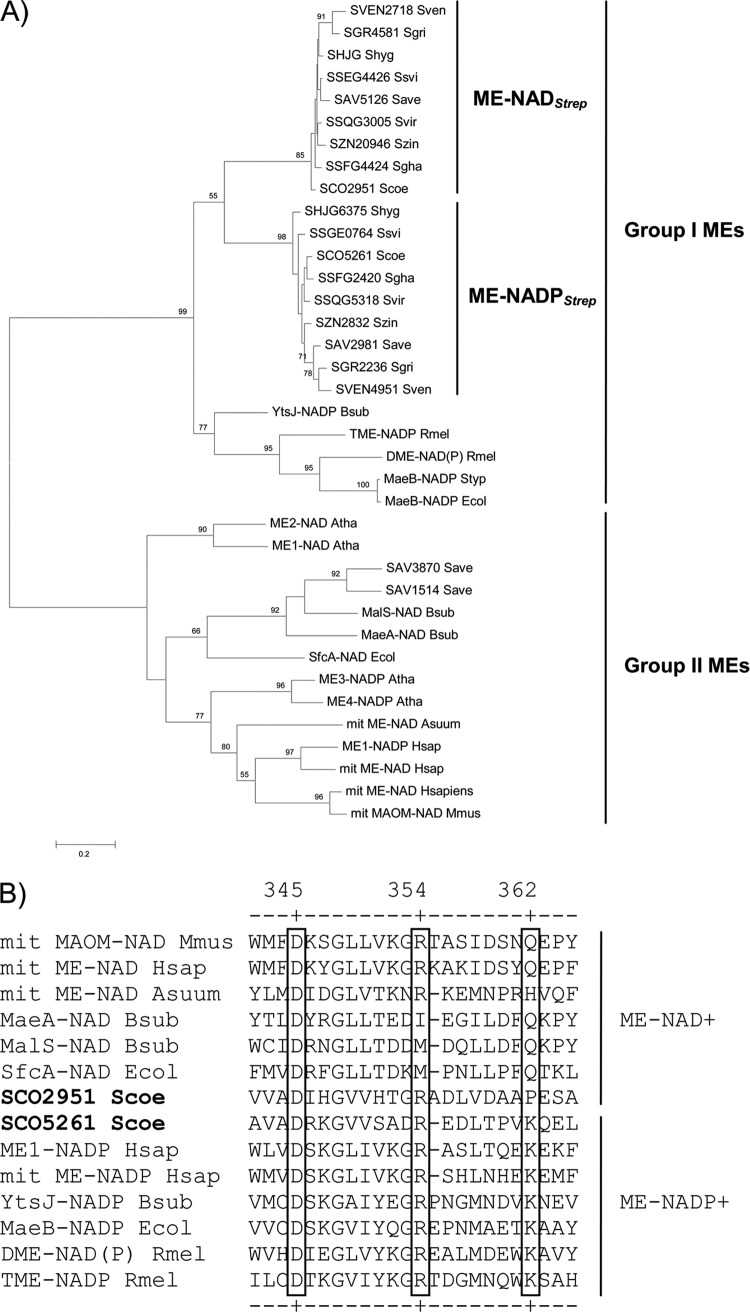
Fig 2.
Phylogenic analysis of malic enzymes. (A) Unrooted phylogenetic tree constituted by 37 ME members from various origins (see Table S1 in the supplemental material for details). Putative gene sequences encoding malic enzymes from Streptomyces spp. were retrieved using Sco2951 and Sco5261 as the query using BLAST (31). The analysis included other prokaryotic and eukaryotic malic enzymes for which cofactor preference is known. The evolutionary history was inferred by using the maximum likelihood method based on the Dayhoff matrix-based model (34). (B) Multiple amino acid sequence alignments of the cofactor binding region in the active sites of malic enzymes using ClustalW (21). Residue numbers correspond to the human mitochondrial NAD+-ME. Residues involved in the adenosine binding site of the cofactor are shown in a box.