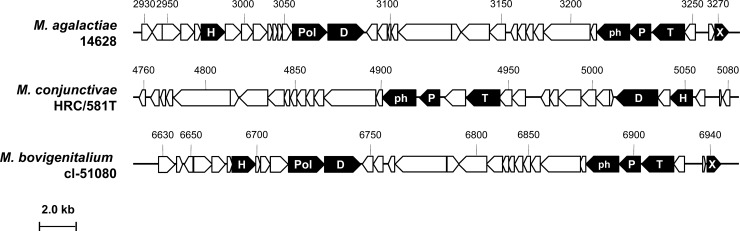
Fig 2.
Genome organization of the prophage identified in strains M. agalactiae 14628, M. conjunctivae HRC/581T, and M. bovigenitalium cl-51080. The locations, sizes, and orientations of the CDSs identified in each prophage are indicated by arrows. CDS numbers refer to the mnemonic codification used for each mycoplasma in the databases (see Table S2 in the supplemental material). CDSs encoding common phage products are highlighted in black using the following letter code: H, helicase; Pol, DNA polymerase; D, DNA primase; ph, prohead protein; P, portal; T, terminase; X, Xer. The overall organization of the prophages is similar, with some differences in M. conjunctivae HRC/581T, including the inversion of the region from MCJ_005050 to MCJ_005030, the absence of a DNA polymerase gene, and the absence of a recombinase gene (xer).