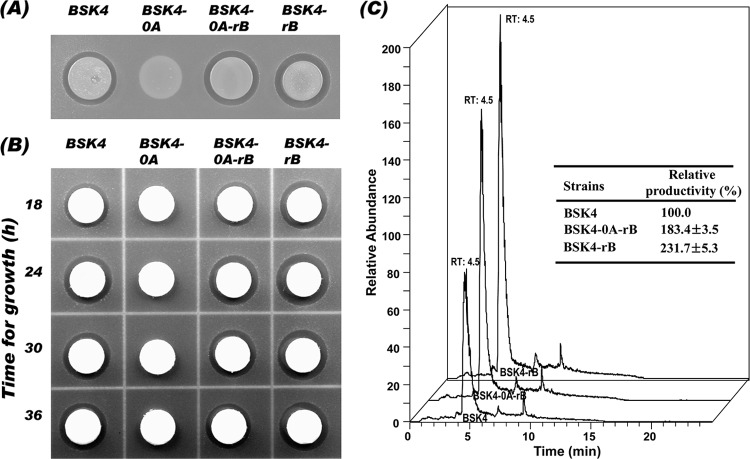
Fig 2.
Antibacterial activities of spo0A or abrB mutant strains derived from BSK4 against E. coli (A and B) and quantitative HPLC analysis of polymyxin produced by the strains after growing for 24 h (C). The B. subtilis strains BSK4, BSK4-0A, BSK4-0A-rB, and BSK4-rB were grown in Cal18 medium for 18, 24, 30, and 36 h. A culture aliquot (5 μl) of each strain grown for 24 h was dropped directly onto E. coli plates containing E. coli cells (∼106 CFU/ml) for antibacterial assay (A), and 50 μl of cell-free supernatant of each strain harvested at different growth times was loaded onto a paper disk and transferred to the E. coli plates (B). The growth inhibition was observed after 24 h of incubation at 37°C. (C) The 24-h culture samples were used for quantitative analysis of polymyxin by ESI-LC/MS, and the [M + 2H]2+ ion peaks of 579.5 m/z were obtained. The areas of the ion peaks were determined for comparison with each other.