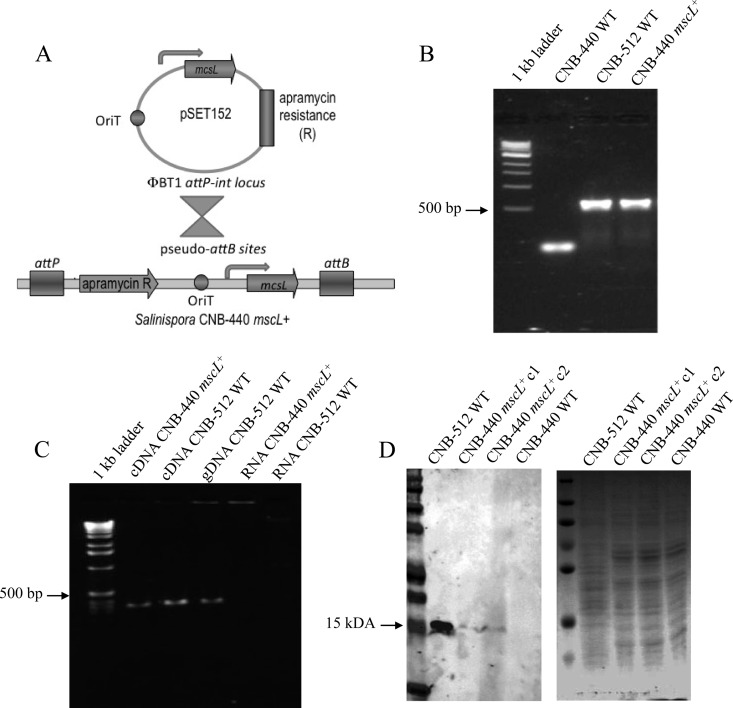
Fig 2.
Complementation experiments. (A) Diagram of the conjugation assay in which an E. coli donor strain harboring the Micromonospora CNB-512 mscL gene (S17-1/ pSET152::mscL) was used to introduce mscL into the recipient S. tropica CNB-440 strain. (B) PCR amplification of the mscL genes from S. tropica CNB-440 mscL+ and Micromonospora CNB-512, using the primer set EcoRI-mscL-ext-F/R (580-bp product). No appropriately sized product was observed from the CNB-440 WT strain. (C) PCR amplification of the mscL gene from cDNA generated from the CNB-440 mscL+ transformant and both cDNA and genomic DNA (gDNA) generated from Micromonospora strain CNB-512, using the primer set mscL-int-F/R (320-bp product). No products were observed from RNA controls. (D) Western blot analysis reveals the association of MscL with a membrane-enriched subcellular fraction as detected using an MscL-specific polyclonal antibody. The arrow shows the expected size of the protein, which was detected in relatively low quantities in two CNB-440 mscL+ transformants relative to the CNB-512 WT strain. The SDS-PAGE profile of the same samples stained with Coomassie blue shows that they contain similar protein concentrations.