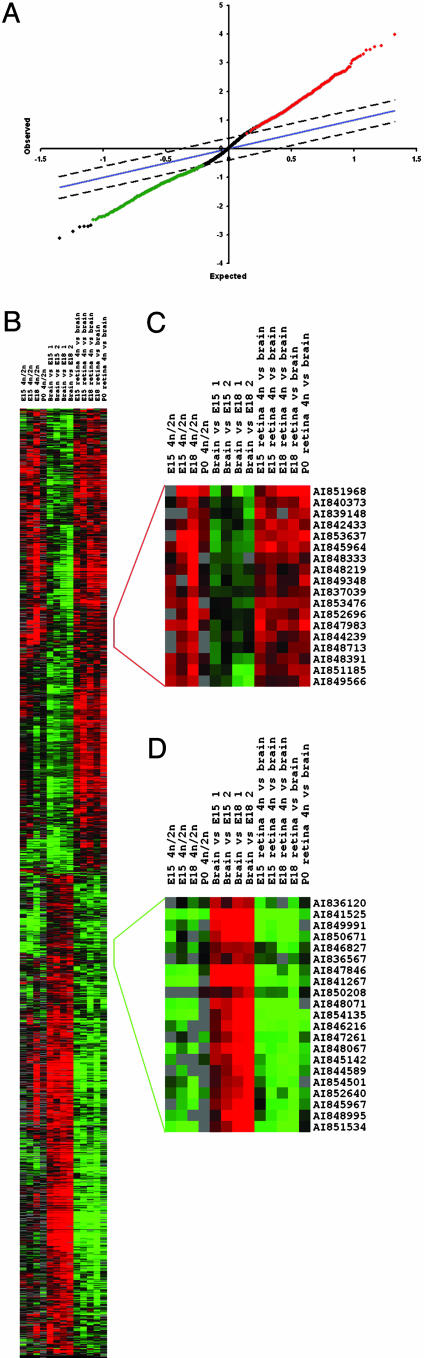
Fig. 2.
Identification of a set of transcripts enriched in FACS-purified retinal progenitor cells. (A) Significance analysis of microarrays plot of the distribution of expected and observed values for gene expression ratios. Genes found to be reproducibly enriched in expression in 4N (progenitor) cells compared to brain and retinal 2N cells (neurons and progenitors) are highlighted in red, those expressed at a lower level in 4N cells are in green. (B) Hierarchical clustering of the results from A. (C) Detail of the hierarchical cluster analysis from A, showing genes enriched in expression in 4N cells compared to both brain and 2N cells. Note that, in addition to 4N/2N and 4N/brain hybridizations, brain/4N or dye-swap hybridizations were also included both as technical replicates and to control for dye-dependent biases within the hybridizations. In this and subsequent cluster diagrams, each row illustrates the gene expression ratios for a single gene, and each column represents a single array hybridization. The samples used for each hybridization are shown at the top of each column, with the Cy5-labeled sample listed first. By convention, the intensity of the color of each gene expression representation is proportional to the magnitude of the gene expression ratio, with red representing genes expressed at higher levels in the Cy5-labeled sample, green those expressed at a higher level in the Cy3-labeled sample, and black those expressed equally between the samples. (D) Detail of the hierarchical clustering of the results from A, showing genes enriched in expression in brain and 2N cells compared to 4N cells. This cluster includes several genes encoding synapse-associated proteins.