Fig 6.
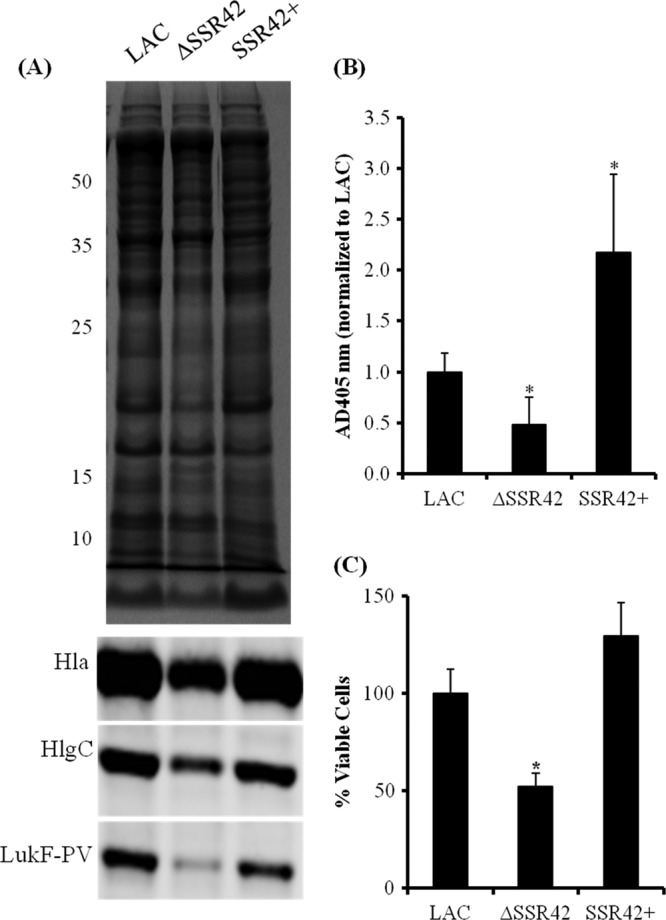
SSR42 affects extracellular virulence factor expression and pathogenesis phenotypes. (A) Stationary-phase culture supernatants from LAC, ΔSSR42, and SSR42+ cells were separated using SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue for assessment for equally loaded amounts of protein. The supernatants were subsequently probed for LukF-PV, Hla, and HlgC. (B) Hemolytic capabilities of stationary-phase culture supernatants from LAC, ΔSSR42, and SSR42+ were quantified as measurements of A405 due to heme liberated from lysed rabbit erythrocytes. Error bars represent 1 standard deviation from the mean (n = 5). (C) S. aureus neutrophil survival assay assessed the abilities of LAC, ΔSSR42, and SSR42+ cells to survive in the presence of primary human PMNs. Bacterial cells were cultured in the presence of PMNs (MOI = 10) for 3 h, and viable S. aureus cells were determined by serial plating and CFU counting. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (n = 3). In panels B and C, asterisks represent statistical significance (P < 0.05) determined by multiple comparisons of means with a Bonferroni-Holm correction. Error bars represent 1 standard deviation from the mean for each sample. The values to the left of panel A are molecular sizes in kilodaltons.
