Fig 6.
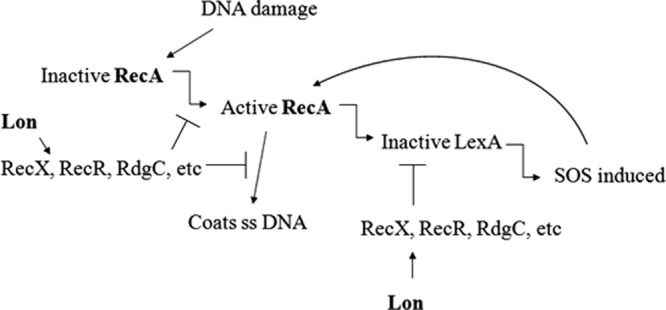
Proposed model for the involvement of the Lon protease in the DNA damage response. Under DNA-damaging conditions, the Lon protease is proposed to cleave and thus antagonize one or more of RecX, RecR, and RdgC, etc., which are known repressors of RecA in E. coli (8, 9, 32, 36). This inhibition leads to autoamplification of RecA, and the SOS response is induced. However, if the Lon protease is inactive, the repressors are proposed to inhibit RecA function and autoamplification.
