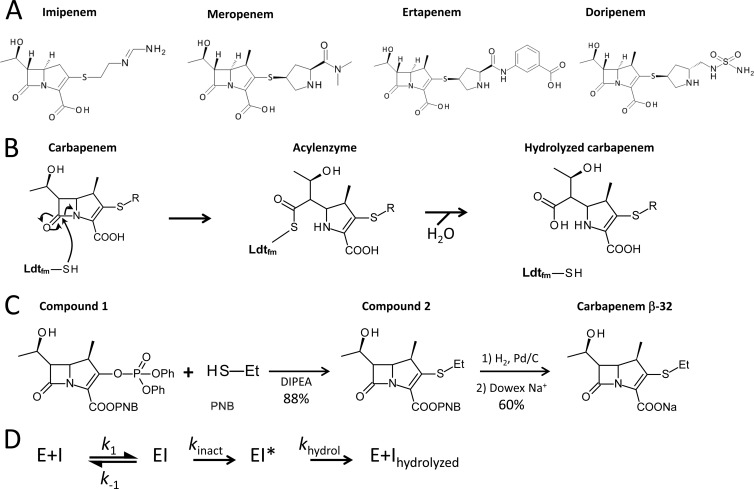
Fig 1.
(A) Structures of carbapenems. (B) Mechanism of inactivation of E. faecium l,d-transpeptidase (Ldtfm) by carbapenems. The sulfhydryl (SH) of the active-site cysteine of Ldtfm attacks the carbonyl of the β-lactam ring to form a covalent adduct (acyl enzyme). Hydrolysis of the resulting thioester bond leads to native enzyme and hydrolyzed carbapenem. R, carbapenem side chain. (C) Synthesis of carbapenem β-32. An addition-elimination reaction in N,N-diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) afforded compound 2 from commercially available compound 1 with an 88% yield (15). Palladium-catalyzed (Pd/C) hydrogenation followed by ion exchange (Dowex resin) (15) afforded the sodium salt of carbapenem β-32 with a 60% yield. Et, ethyl; PNB, paranitrobenzoate. (D) Reaction scheme used in kinetic analyses. Binding of carbapenem (I) to Ldtfm (E) leads to reversible formation of a noncovalent complex (EI). Formation of the acyl enzyme (EI*) and its hydrolysis are irreversible. k1 and k−1 are second- and first-order constants for formation and dissociation of the noncovalent complex. kinact and khydrol are the rate constants for the acylation and hydrolysis reactions.