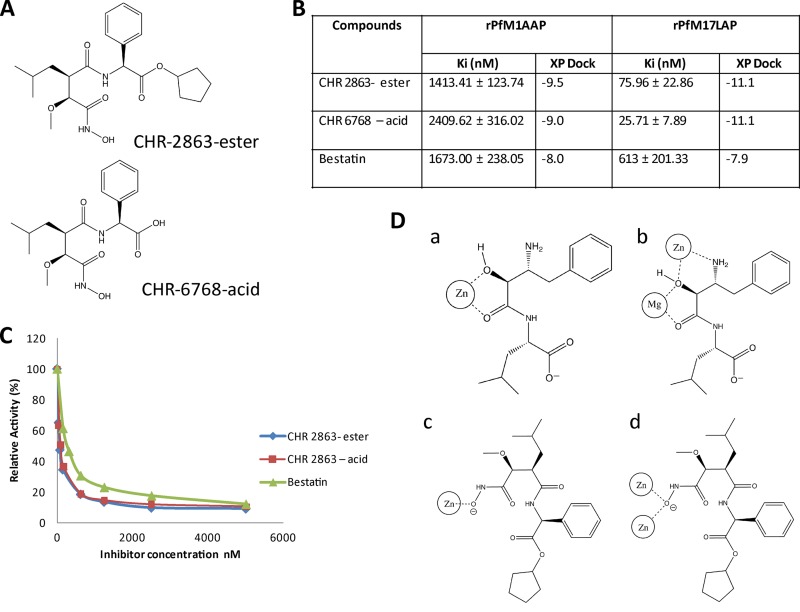
Fig 1.
Structure, enzyme kinetics, and binding mode of the novel aminopeptidase inhibitor CHR-2863. (A) CHR-2863 and CHR-6768. (B) Ki values and XP dock scores of CHR-2863 and CHR-6768 compared to those of bestatin when assessed against rPfM1AAP and rPfM17LAP. (C) Inhibition curves of aminopeptidase activity in malaria extracts. The substrate (H-Leu-NHMec) was maintained at 25 μM, while the inhibitor compounds were varied. Soluble malaria extract was prepared as previously reported (21), and 5 μg total proteins was used in each assay. (D) Schematic representations of metal-ligand interaction diagrams for rPfM1AAP and rPfM17LAP illustrating the different cavity binding orientations observed in the solid state for bestatin and the proposed structures for CHR 2863 based on docking analysis. (a) rPfM1AAP and bestatin (derived from X ray data; PDB code 3EBH); (b) rPfM17LAP and bestatin X-ray (derived from PDB code 3KR4); (c) rPfM1AAP docked with CHR-2863; (d) rPfM17LAP docked with CHR-2863.