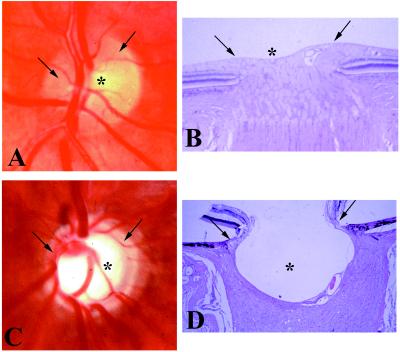
Figure 1.
Human optic nerve head. (A and C) In vivo photograph. (B and D) Postmortem photomicrograph. (Hematoxylin and eosin stain; ×20.) (A and B) Normal. (C and D) Advanced glaucoma. Note the small, shallow central physiologic “cup,” (asterisk) and the full neuroretinal rim (arrow) (which comprises approximately 106 axons) in the normal nerve head. Compare with the deep, wide central excavation, the nasal displacement of the blood vessels, and the narrowing of the neuroretinal rim, indicating loss of most optic nerve fibers and their retinal ganglion cells, in the glaucomatous eye.