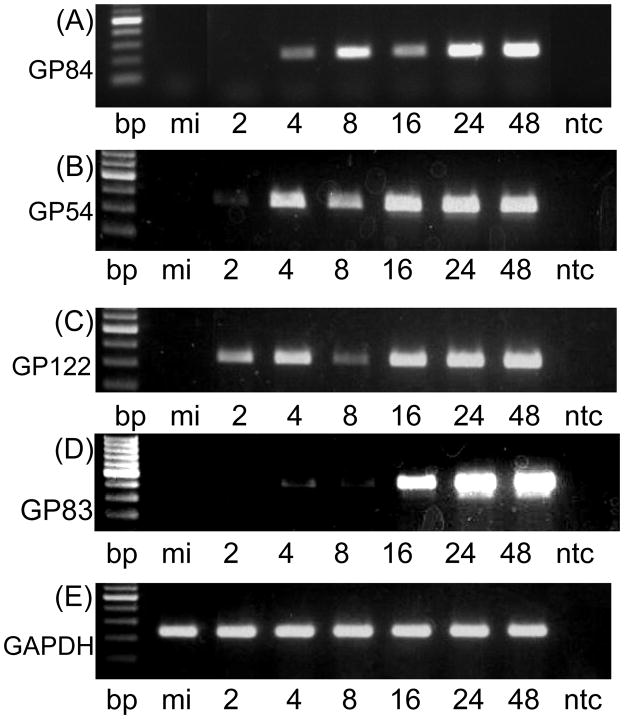
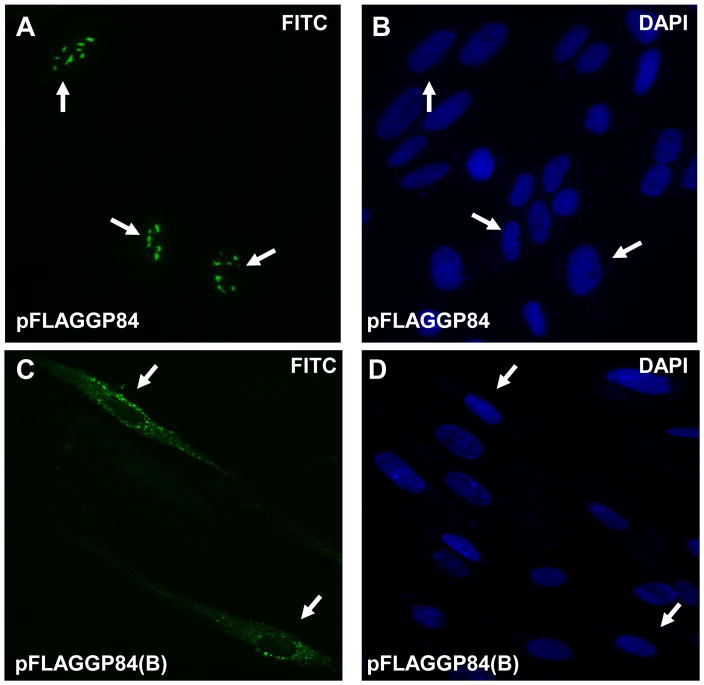
Figure 1. Expression studies of GP84.
1(i) RT-PCR assay of GP84 mRNA expression in virus infected cells. Wild type virus infected GPL cells (moi=3 pfu/cell) were harvested at different time points for RNA extraction and mRNA analysis by RT-PCR using GP84, GP54 (viral polymerase), GP122 (IE2 unique exon) and cellular GAPDH specific primers as described in materials and methods. Viral gene classes: immediate early, IE2, unique exon GP122 (Yamada et al., 2009); early, viral polymerase GP54 (Schleiss, 1995); and late, GP83, encoding pp65 homolog (Schleiss et al., 1999). RT-PCR products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis: GP84 (gel A); GP54 (gel B); GP122 (gel C); and GAPDH control (gel D). In all gels lanes are as the same. 100 bp ladder (NEB) followed by mock infected cells (mi), time samples 2–48 hr post infection (hpi) and no template control (ntc). Time samples 2, 4, 8, 16, 24 and 48 hr post infection.
1(ii) Transient expression studies of full length and N-terminal truncated GP84. Immunofluorescence assay of FLAG-tagged GP84 protein transiently expressed in GPL cells transfected with pFLAGGP84 or pFLAGGP84(B). Assay performed at 10 hr post transfection. Primary antibody anti-FLAG and secondary antibody anti-mouse IgG conjugated to FITC (images A and C). Cells counterstained with DAPI (images B and D). Arrow indicates same cell under FITC and DAPI filters. Images A and B, full length pGP84 (pFLAGGP84 plasmid). Images C and D, N-terminal truncated pGP84 (pFLAGGP84(B) plasmid).