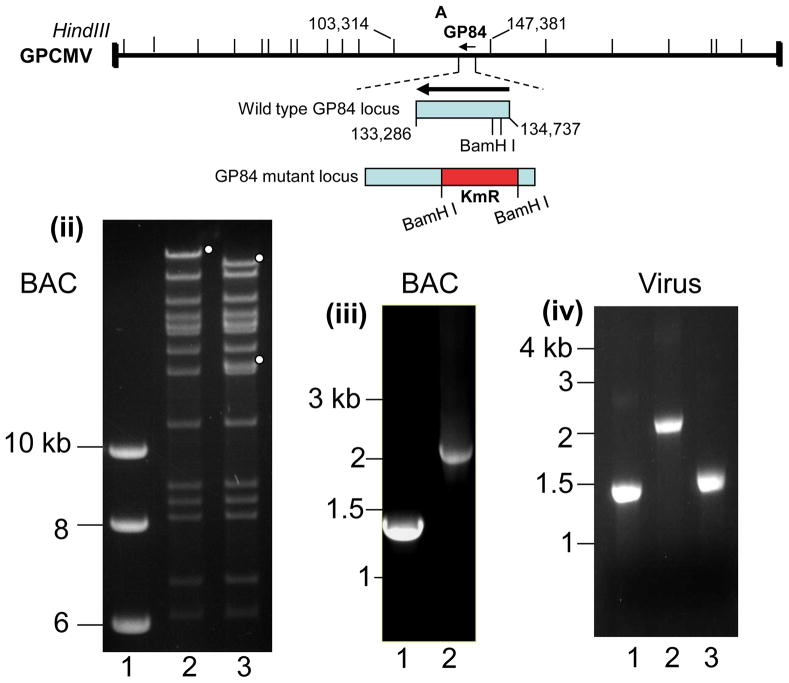
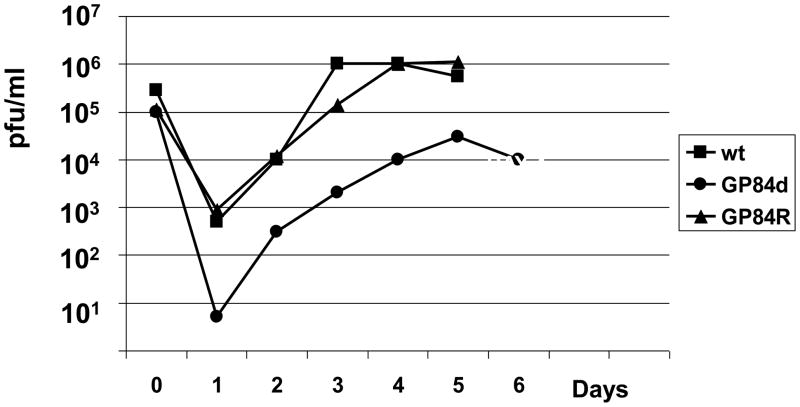
Figure 4. Characterization of GP84 knockout GPCMV mutant (GP84d).
(i) GPCMV genome map of Hind III sites and the location of the knockout GP84 gene. Shown is the GPCMV Hind III ‘A’ locus (co-ordinates 103,314–147,381 bases) encoding GP84 CDS (complement 133,286–134,737 bases). Insertion of a kanamycin resistance cassette into the GP84 coding sequence between two BamH I sites (134,097 and 134,314 bases) results in an insertion deletion disruption of the GP84 coding sequence.
(ii) Wild type and GP84 mutant GPCMV BAC Hind III restriction profile analysis.Agarose gel of the DNA restriction profile analysis of mutant and wild type GPCMV BACs. Lanes: 1. kb ladder (NEB). 2. wt GPCMV BAC; 3. GP84d GPCMV BAC. Insertion of a kanamycin cassette into the GP84 gene introduces a new Hind III site into the GPCMV genome and disrupts the Hind III ‘A’ band encoding the GP84 gene. Full length (lane 2) and modified bands encoding part of the Hind III ‘A’ band (lane 3) are indicated with circles.
(iii) GPCMV BAC Diagnostic PCR analysis of the GP84 locus.Common primers flanking the site of modification in the GP84 locus were used to verify the modification to the GP84 locus in comparison to the wild type locus. Shown is an agarose gel of GP84 PCR products from different BAC DNA templates. Lanes: 1. wt GPCMV BAC; 2. GP84d GPCMV BAC mutant. Shift in the size of the locus confirms correct insertion of the kanamycin cassette plus deletion of GP84 sequence between BamH I sites.
(iv) Viral DNA Diagnostic PCR analysis of the GP84 locus. Common diagnostic GP84 locus primers were used to confirm the status of the GP84 locus in viral genomes: 1. wt GPCMV; 2. GP84d mutant; 3. GP84d rescue virus. The mutant virus retains the same modification generated in the GPCMV BAC mutant and the rescue virus has a wild type sized GP84 locus.
(v) Multi step growth curve of GPCMV GP84 mutant (GP84d)Growth curve performed as described in materials and methods. GPCMV GP84 knockout mutant (GP84d) was compared to wild type GPCMV (wt) and GP84d rescue virus (GP84R). Input virus moi was 0.1 pfu/cell with time points taken at 24 hr. intervals between 0–6 days post infection.