Figure 5. Generation and characterization of GP84 chimeric HCMV.
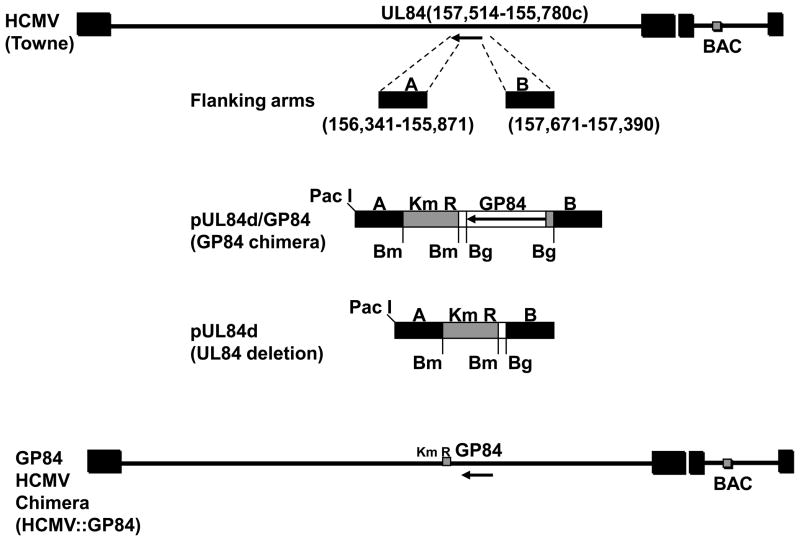
(i) Overall strategy for the generation of UL84 knockout and GP84 chimera HCMV BAC mutants. Construction of UL84 knockout shuttle vectors. UL84 flanking sequence was generated by PCR (right arm left arm, A and B). For UL84 deletion HCMV BAC a BamH I Km cassette was cloned into the shuttle vector to generate pUL84d. For generation of the GP84 chimeric HCMV the FLAG tagged GP84 ORF from pFLAGGP84 was PCR cloned as a Bgl II cassette 5’ to the Km cassette in plasmid pUL84d to generate construct pUL84d/GP84. Shuttle vectors were linearised by Pac I digestion prior to recombination in bacteria with HCMV Towne BAC following protocol described by McGregor et al. (2004). Structure of GP84 HCMV chimeric virus is shown in the bottom of the figure.
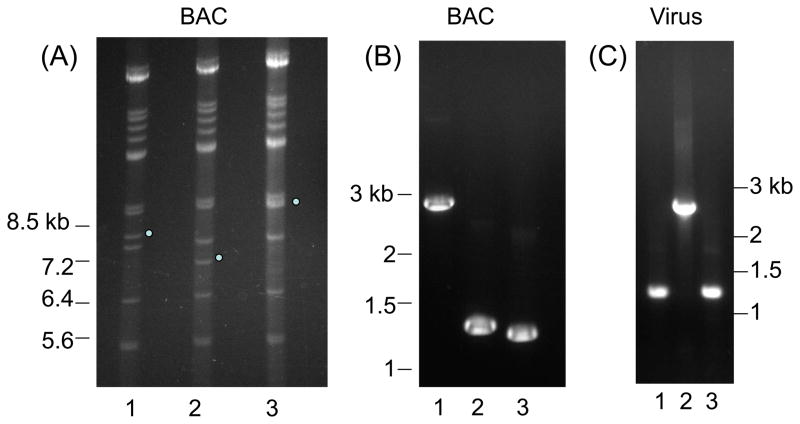
(ii). Analysis of HCMV wild type and UL84 mutant structures. (A) HCMV BAC DNA Hind III restriction profiles. Lanes: 1. wt HCMV BAC DNA; 2. UL84 deletion mutant HCMV BAC DNA; 3. GP84 chimera HCMV BAC DNA. Dots mark wild type or modified 7.8 kb Hind III subgenomic fragment (co-ordinates 120,817–128,615 HCMV Towne) encoding the UL84 wild type locus (lane 1) and modified by the deletion of the majority of the UL84 coding sequence and insertion of a Km cassette (UL84 deletion mutant HCMV BAC, lane 2) plus the insertion of the GP84 coding sequence (GP84 HCMV chimera BAC, lane 3).
(B) PCR analysis of wild type and mutant UL84 loci from HCMV BAC clones. Common PCR primers amplified the modified UL84 locus from the HCMV BAC constructs and PCR products were analysed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Lane: 1. GP84 chimeric HCMV BAC; 2. wild type HCMV BAC; 3. UL84 deletion HCMV BAC.
(C) PCR analysis of wild type and mutant UL84 loci from viral DNA. Common PCR primers amplified the modified UL84 locus from wild type and GP84 chimeric HCMV viral DNA and PCR products were analysed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Note that the rescue virus was generated to the lethal UL84 knockout. Lane: 1. wild type HCMV; 2. GP84 HCMV chimera; 3. UL84 deletion rescue virus. Diagnostic PCR confirms that the chimeric virus encodes a modified UL84 locus similar to the GP84 HCMV chimeric BAC (B, lane 1).
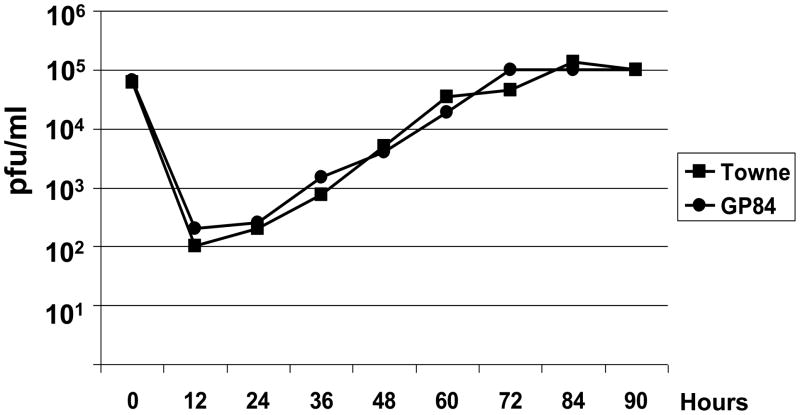
(iii) One step growth curve of wild type HCMV (Towne) and GP84 chimeric HCMV. Growth curve carried out as described in materials and methods with an initial input of virus of 3 pfu/cell (moi) with time point samples taken every 12 hr (0–90 hr post infection) as described in materials and methods.
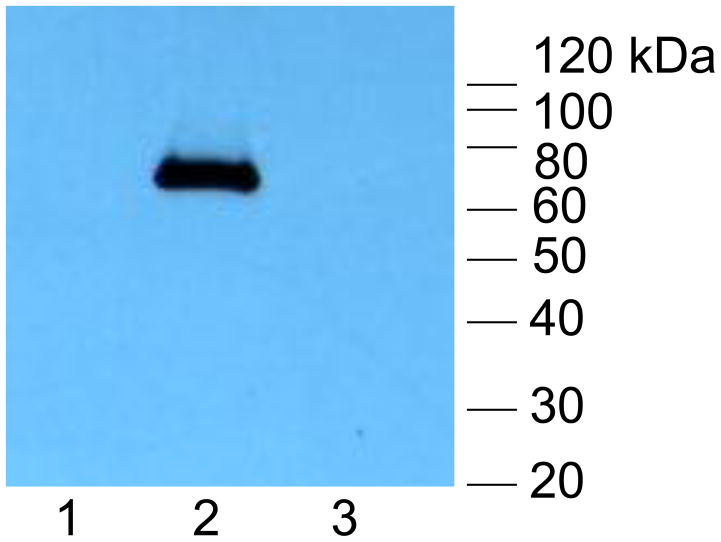
(iv) Western blot of FLAG-tagged GP84 protein expressed in chimeric virus infected cells. Lanes: (1) Mock infected HFF cells; (2) GP84 chimeric virus infected cells; (3) HCMV (Towne) infected cells. Protein ladder (Invitrogen). GP84 protein detected with primary antibody mouse anti-FLAG and secondary anti-mouse IgG conjugated to HRP as described in materials and methods.