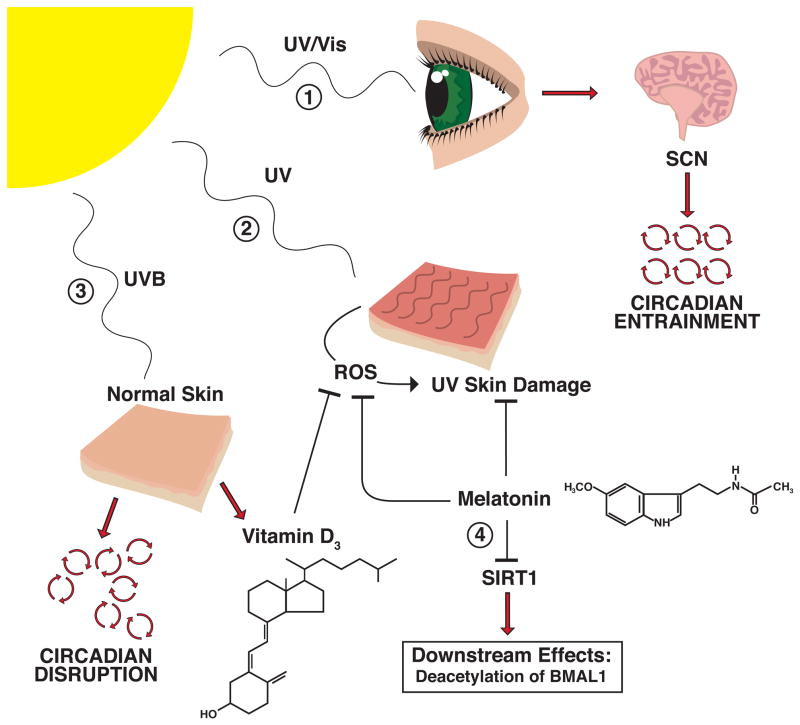
Figure 2. Light, Circadian Rhythms, and Melatonin.
1) UV or visible light from the sun is sensed by the retina, which signals the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) region of the brain, enabling entrainment of circadian rhythms throughout the body. 2) UV light induces skin damage. Both Melatonin and Vitamin D3 have protective effects against this damage, through the inhibition of reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation as well as other mechanisms. 3) UVB light exposure can cause disruption of the circadian rhythms in normal skin, but also has the protective effect of producing Vitamin D3. 4) In addition to its protective effects against UVB skin damage, melatonin also plays a role in the regulation of circadian rhythms, through its inhibition of the HDAC SIRT1.