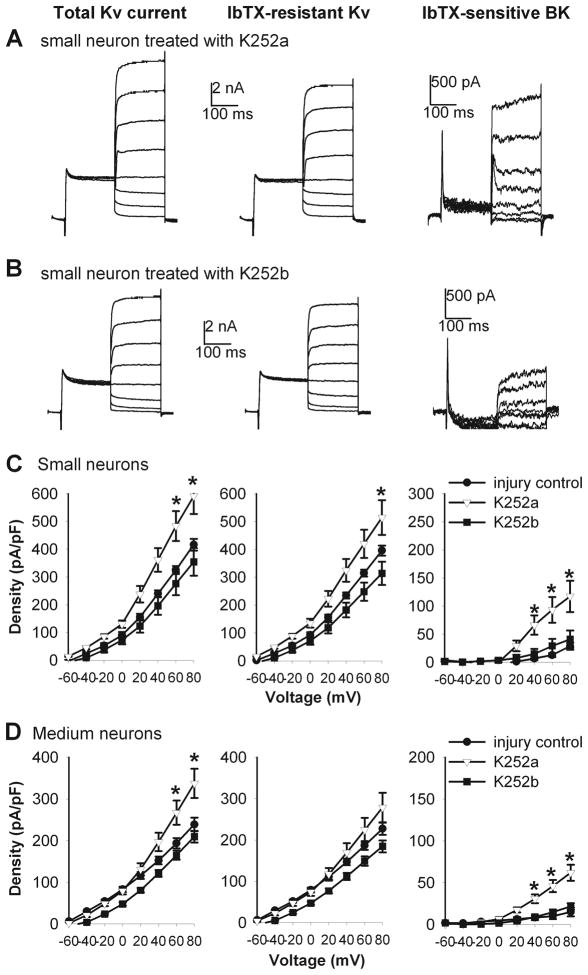
Figure 9.
K252a reversed the effects of nerve injury on the total Kv, IbTX-resistant Kv, and IbTX-sensitive BK currents in small and medium DRG neurons. A and B, original current traces show that the differential effects of K252a and K252b on the total Kv, IbTX-resistant Kv, and IbTX-sensitive BK currents in small DRG neurons from a nerve-injured rat. C, group data show that K252a (n = 7), but not K252b (n = 11), reversed the effects of nerve injury on the total Kv, IbTX-resistant Kv, and IbTX-sensitive BK currents in small DRG neurons. D, summary data show that K252a (n = 11), but not K252b (n = 13), reversed nerve injury-induced reduction in the total Kv, IbTX-resistant Kv, and IbTX-sensitive BK currents in medium DRG neurons. * P < 0.05 compared with the corresponding value in the injury control group.