Fig. 5.
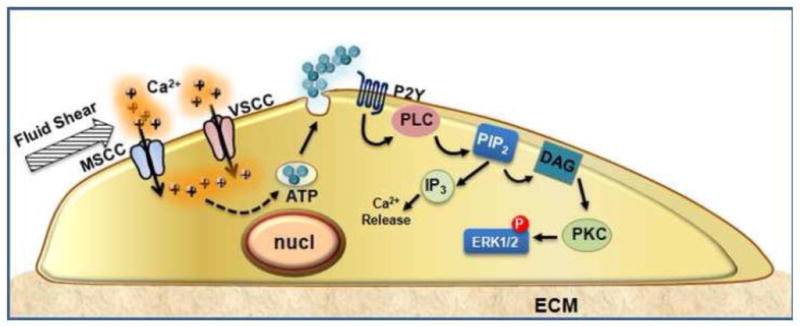
Calcium channels and purinergic signaling cooperate to regulate mechanosensitive functions in bone cells. Fluid shear stress activates a mechanosensitive channel in the plasma membrane, leading to local membrane depolarization sufficient to induce Ca2+ influx through the VSCC complex. Acting as a second messenger, Ca2+ facilitates vesicular fusion and release of ATP. Acting in an autocrine/paracrine fashion, ATP stimulates purinergic receptors that activate PLC and ERK1/2 pathways in response to mechanical signals.
