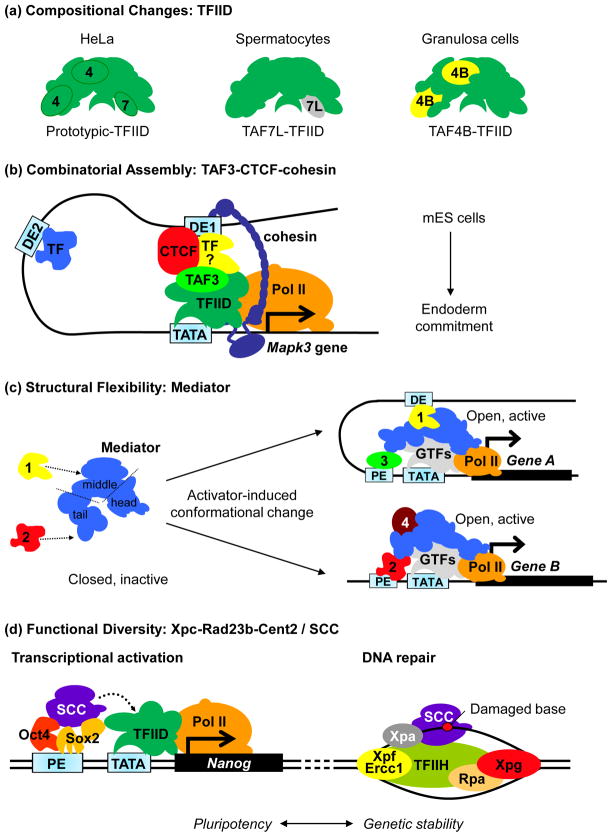
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of cell type-specific transcriptional activation by coactivators. (a) Prototypic TFIID purified from HeLa cells is composed of the TATA-binding protein (TBP) and 13–14 TBP-associated factors (TAFs). Canonical TAFs are replaced with gonad-selective TAFs in both male and female germ cells. TAF7 is substituted with its paralog TAF7L in spermatocytes while TAF4 is replaced with TAF4B in granulosa cells of the ovary. Genetic inactivation of TAF7L and TAF4B in mice led to sterility. Incorporation of non-canonical TAFs like TAF7L and TAF4B in TFIID may provide unique contact surfaces for germ cell-specific transcription factors to mediate transcriptional activation [9]. (b) In mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells, the combinatorial assembly of TAF3, CTCF (CCCTC-binding factor), cohesin and presumably an endoderm lineage-specific TF (yellow) permits selective long distance enhancer-promoter DNA interaction (via DE1 but not DE2) that leads to activation of the Mapk3 (mitogen-activated kinase 3) locus and endoderm commitment during ES cell differentiation. (c) Binding of transcription factors (TFs) to Mediator induces conformational changes that convert Mediator from an inactive, closed conformation to an open, transcriptionally competent one, which in turns, facilitates additional contacts with other TFs occupied at the proximal (PE) or distal (DE) enhancers as well as the general transcription machinery (general transcription factors, GTFs, and RNA polymerase II, Pol II) assembled on a gene promoter (TATA). The modular nature of Mediator provides unique contact surfaces for diverse TFs. In the hypothetical example depicted above, recruitment of Mediator to the DE of Gene A by TF1 via the middle module causes a conformational change in Mediator that exposes unique, TF1-dependent interacting surfaces for Pol II and PE-bound TF3. On the other hand, activation of Gene B involves the binding of TF2 to Mediator tail at PE. TF2-induced conformation change in Mediator exposes new docking sites for another coactivator (“4”) and the general transcription machinery [69]. (d) In ES cells, the Xpc-Rad23b-Cetn2 complex (SCC) functions both as a coactivator for Oct4 and Sox2 at the Nanog gene, and as an initiator of global genome-nucleotide excision repair (GG-NER) by binding to specific DNA lesion and recruiting other NER factors (Xpa, Rpa, TFIIH, Xpg and Xpf-Ercc1). SCC may function to couple stem cell-specific transcription with genome surveillance.