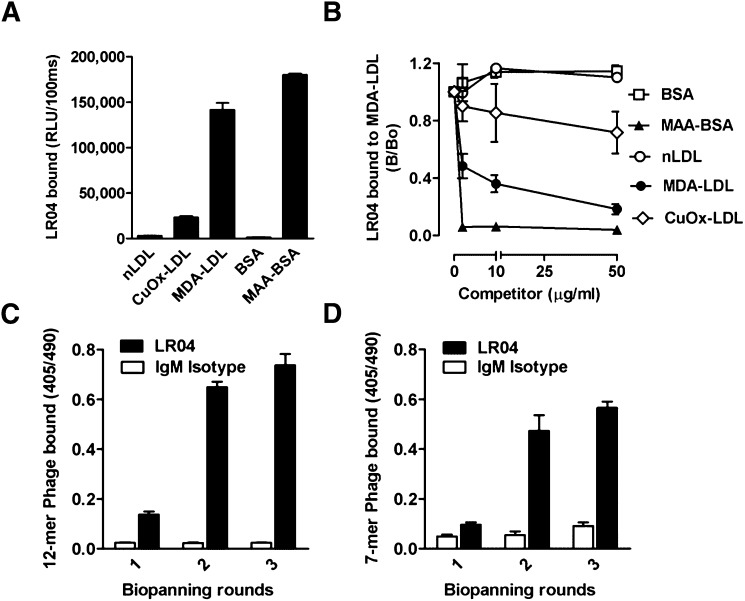
Fig. 1.
Biopanning of phage display peptide libraries with monoclonal antibody LRO4. (A) ELISA for the binding of the murine IgM mAb LRO4 (5 μg/ml) to native LDL (nLDL), CuOx-LDL, MDA-LDL, BSA, and MAA-modified BSA. Values are given as relative light units (RLU) per 100 ms and represent the mean ± SD of triplicate determinations. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (B) Competition immunoassay for the specificity of LRO4 binding to MDA-LDL. Data are expressed as a ratio of binding in the presence of competitor (B) divided by absence of competitor (B0) and represent the mean ± SD of triplicate determinations. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (C, D) ELISA for the binding of eluted phages to LRO4. After each round of biopanning, the binding of 1010 pfu/ml phage amplificates from the Ph.D.-12 library (C) and the Ph.D.-C7C library (D) to LRO4 (black bars) and an isotype control IgM (white bars) was tested as described in Materials and Methods. Values are given as absorbance measured at 405 and 490 nm and represent the mean ± SD of triplicate determinations.