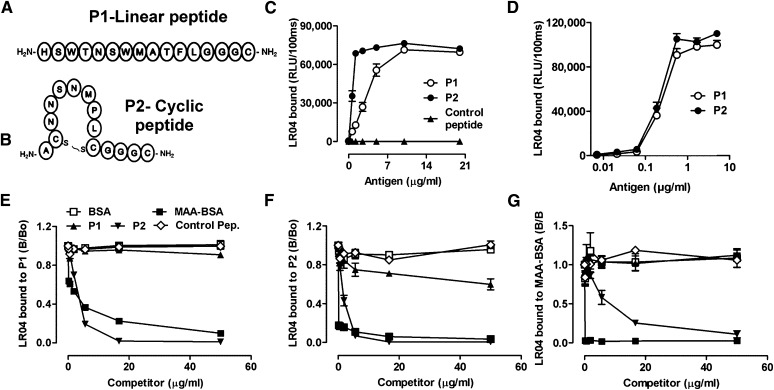
Fig. 2.
Linear P1 and cyclic P2 peptides mimic a specific MDA epitope. (A, B) Schematic representation of synthesized peptides carrying the consensus sequence from phages identified with the Ph.D.-12 and Ph.D.-C7C libraries, respectively. P1(A) is a linear dodecameric peptide ( HSWTNSWMATFL ), and P2 (B) is a cyclic heptameric peptide (C NNSNMPL C). The peptides’ C terminus containing a GGGC-spacer was amidated. (C, D) ELISA for the binding of LRO4 to P1 and P2. (C) Binding of LRO4 to P1 and P2. Peptides P1, P2, and an irrelevant control peptide were coated at indicated concentrations. Binding of LRO4 (5 μg/ml) was determined by chemiluminescent ELISA. (D) Indicated concentrations of biotinylated peptides were captured on wells precoated with 10 μg/ml of neutravidin, and binding of LRO4 (5 μg/ml) was determined as described in Materials and Methods. Values are given as relative light units (RLU) per 100 ms and represent the mean ± SD of triplicate determinations. (E–G) Immunocompetition assays for the antigenic properties of P1 and P2. Binding of 0.5 μg/ml LRO4 to 100 ng/ml captured biotinylated peptides P1 (E) or P2 (F) or to 0.5 μg/ml coated MAA-BSA (G) was measured by ELISA in the presence of increasing concentrations of indicated competitors. Data represent the mean ± SD of triplicate determinations and are representative of three independent experiments.