Figure 1.
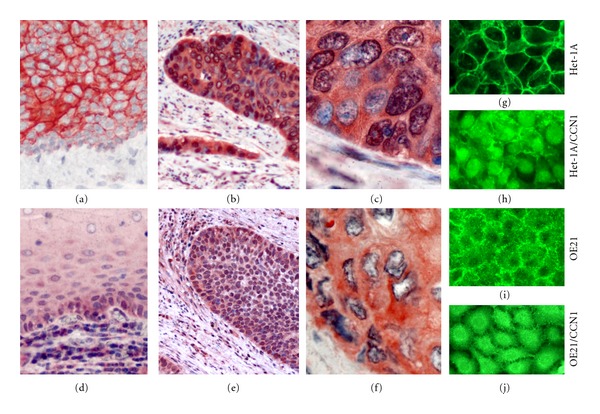
CCN1 induces β-catenin translocation in esophageal epithelial cells. (a) In normal esophageal mucosa, β-catenin is localized to the cell membrane (250x). (b) In ESCC tumor tissue, β-catenin expression is highly elevated (250x). (c) β-catenin in ESCC tissue is mainly localized in the cytoplasm and some appears in the nucleus as well (600x). (d) In normal esophageal mucosa, CCN1 is primarily expressed in the basal cells (250x). (e) CCN1 expression is elevated in ESCC tumor tissue (250x). (f) CCN1 is localized to both cellular and extracellular matrix in ESCC tumor tissue (600x). (g) In Het-1A cells, β-catenin is neatly confined to intercellular connections. (h) Under CCN1 treatment, β-catenin in Het-1A cells accumulates in the cytoplasm and the nucleus. (i) In OE21 cells, β-catenin appears in both the cytoplasm and the cell membrane. (j) Under CCN1 treatment, β-catenin in OE21 cells becomes more concentrated in the nuclear area.
