Figure 7.
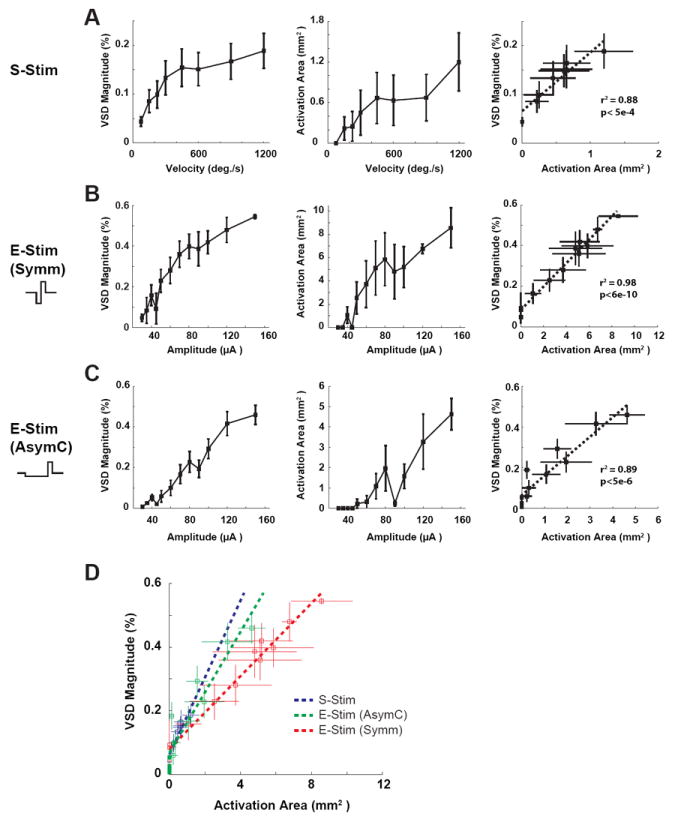
Cathode-leading asymmetric waveform also improved the specificity of thalamic microstimulation. A) The relationship between increasing angular velocity of the punctate whisker deflection and the magnitude (left) and area (middle) of cortical activation. Right: the approximately linear relationship between the area of activation and the magnitude. B) The relationship between increasing amplitude of the current pulse with symmetric waveform and the magnitude (left) and area (middle) of cortical activation. Right: the approximately linear relationship between the area of activation and the magnitude. C) Same as in B for E-Stim (AsymC). D) The slopes of the relationships between the area and magnitude of activation for S-Stim, E-Stim (AsymC) and E-Stim (Symm). Using the asymmetric waveform resulted in a slope much closer to that of the sensory stimulation (S-Stim).
