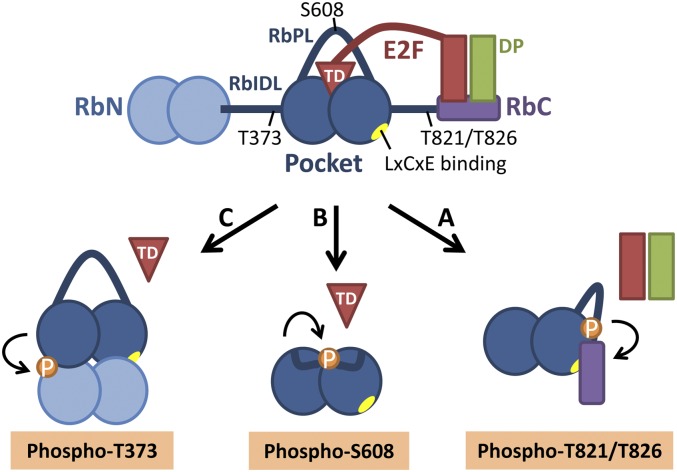
Figure 1.
Cdk phosphorylation of discrete sites in pRb causes distinct conformational changes that inhibit pRb's binding to E2F. (A) Phosphorylation of T821/T826 stabilizes an interaction between the pRb C-terminal domain (RbC) and the pocket and may exclude the E2F–DP complex from RbC (Rubin et al. 2005). (B) Phosphorylation of S608 induces the RbPL to interact with the pRb pocket. This intramolecular interaction competitively blocks the binding of the E2FTD (Burke et al. 2012). (C) Phosphorylation of T373 within the RbIDL stabilizes the docking of the RbN against the pocket. This leads to a rotation of the pocket subdomains relative to one another and allosterically inhibits E2FTD binding to the pocket (Burke et al. 2012). (A,C) The LxCxE-binding cleft in the pocket is blocked by RbN–pocket docking or the RbC–pocket interaction (Rubin et al. 2005; Burke et al. 2012).