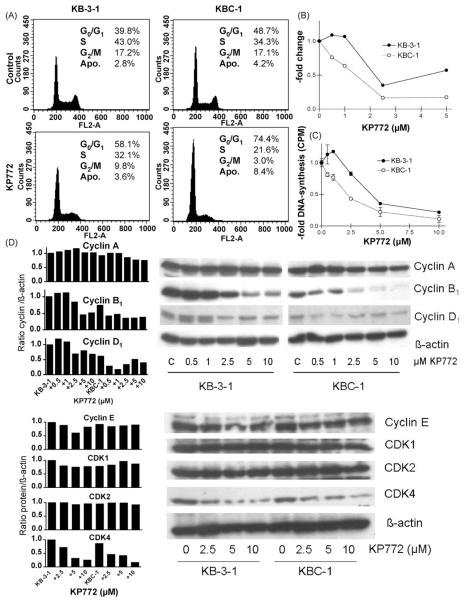
Fig. 2.
Impact of KP772 on cell cycle progression and DNA synthesis of KB-3-1 and ABCB1-overexpressing KBC-1 cells. (A) Changes in the cell cycle distribution of the indicated cell lines treated with 5 μM KP772 for 24 h were analysed by PI staining and FACS. Percentages of cells in G0/G1, S and G2/M phases of the cell cycle as well as apoptotic cells (Apo) are indicated. (B) Changes in the proportion of cells in G2/M phase of the cell cycle at increasing doses of KP772 are shown. The amount of G2/M cells in the untreated control group was set as 1. One of three experiments delivering comparable results is shown. (C) DNA synthesis was determined by 3H-thymidine incorporation after 24 h treatment with KP772 at the indicated concentrations. Values given are means ± S.D. from at least two independent experiments performed in triplicates. (D) The impact of the indicated drug concentrations on the expression pattern of cyclin A, B1, D1, E and CDK1, 2, 4 after a 24 h treatment was analysed by Western blot (right) followed by densiometric evaluation (left). β-Actin was used as loading control. Antibodies are described under Section 2.