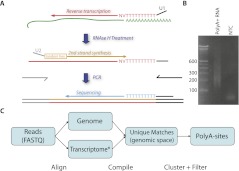
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic overview of PolyA-seq. Input was polyA+ selected RNA (green). Reverse transcription using U1-T10VN was followed by RNase H treatment to degrade RNA. Second-strand synthesis using U2-N6 was achieved through a random-primed Klenow extension. U1 and U2 have sequence complementarity to Illumina-specific adapters, which are added through PCR. This yields DNA libraries that can be directly sequenced. (B) A typical library consists of amplicons ranging from 200 to 500 bp (Illumina adapters account for 79 bp). (NTC) No-template control. (C) Computational procedure: reads were aligned to the genome and transcriptome ([*] defined here as known and predicted splice junctions extracted from UCSC Known Genes, RefSeq, and Ensembl, followed by conversion to genomic coordinates; see Methods for more details). Matches with unique loci were then filtered on internal priming potential and clustered into polyA sites.