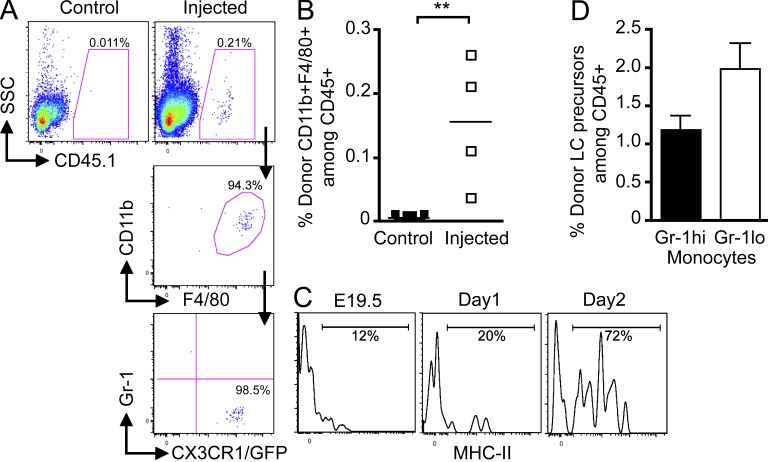
Figure 9.
Fetal liver monocytes contribute to epidermal LCs. Monocytes were purified from E13.5–E14.5 fetal liver of CD45.1+ mice and adoptively transferred in utero into unconditioned E13.5–E14.5 CD45.2+ congenic embryos. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of the progeny of adoptively transferred CD45.1+ monocytes in E19.5 epidermis 5 d after transfer. Control represents noninjected embryos (n = 9). (B) Percentage cells derived from donor monocytes for each injected embryos in the epidermis 5 d after injection. Bars show means of data from one representative experiment of three. (C) Expression of MHC-II on donor CD45.1+ monocyte-derived LC precursors at the indicated time points. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments (n = 2). (D) Percentage E18.5 donor (CD45.1+) LC precursors (CD11b+F480+CX3CR1/GFPhi) derived from adoptively transferred Gr-1hi or Gr-1lo fetal liver monocytes (5 × 105 per embryo). Error bars represent mean ± SEM of pooled data from 2 experiments (n = 2–5).