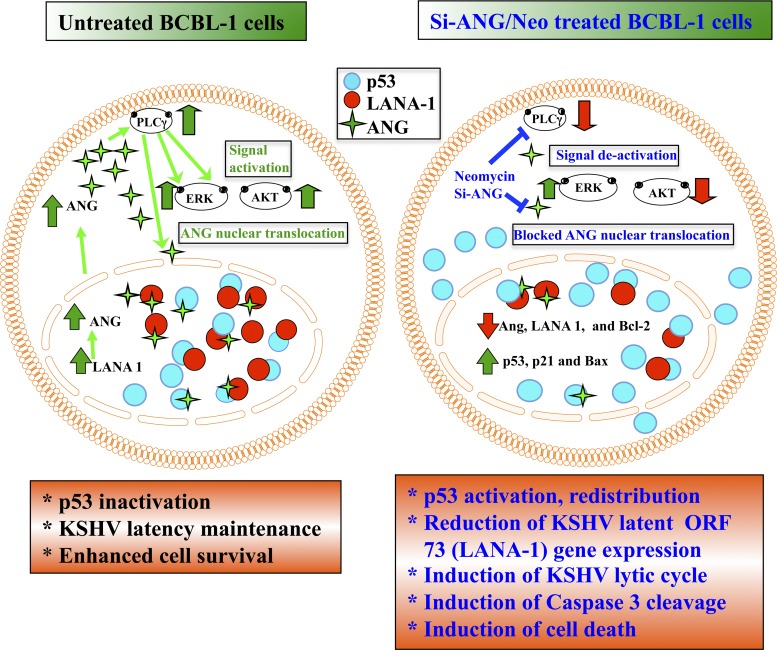
Fig 12.
Schematic model showing the events occurring in B cells latently infected with KSHV in the context of angiogenin and the consequences of silencing angiogenin or inhibiting PLCγ activation by neomycin. In BCBL-1 cells, LANA-1 expression induces ANG, which activates the PLCγ, ERK, and AKT pathways. PLCγ activation is required for the nuclear translocation of ANG. The present study shows that in the nucleus, LANA-1 interacts with ANG and p53 and forms a complex. There are also other complexes consisting of ANG-p53, LANA-1-p53, and LANA-1-ANG. These interactions suppress p53 functions, leading to enhanced cell survival and latency maintenance. When ANG is silenced or its nuclear transport via PLCγ activation is inhibited by neomycin treatment, AKT signaling is decreased while the ERK pathway is unaffected. ANG's nuclear translocation is inhibited, which results in decreased LANA-1 expression; decreased interactions between LANA-1-ANG-p53, LANA-1-p53, ANG-p53, and LANA-1-ANG, leading to the activation of p53; and increased detection of p53 free of ANG and LANA-1 in the cytoplasm, resulting in the induction of apoptosis, KSHV lytic cycle, and cell death.