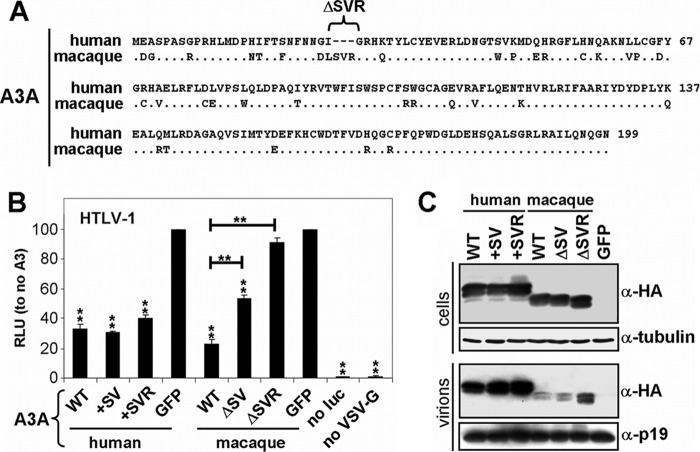
Fig 3.
Comparison between human and macaque A3A restriction of HTLV-1. (A) Protein sequence alignment of human A3A and Macaca mulatta A3A. Human A3A contains a specific deletion of 27S, 28V, and 29R. (B) The indicated A3A WT and mutant expression plasmids were cotransfected with HTLV-1 helper (GagPol and nonstructural proteins), luciferase reporter, and VSV-G plasmids in HEK-293T cells. The cells were overlaid with Jurkat cells, and luciferase (RLU) was measured after 3 days. GFP is set at 100%. Values are means plus standard deviations (error bars) for three independent experiments. P values were computed to determine whether differences between GFP and each A3 protein or between A3A mutants reach significance (P < 0.05 [*] and P < 0.01[**] by unpaired t test using GraphPad Prism 5 software). no luc, no luciferase. (C) The indicated A3A WT and mutant expression plasmids were cotransfected with HTLV-1 helper (GagPol and nonstructural proteins), luciferase reporter, and VSV-G plasmids in HEK-293T cells, and the cells were lysed 2 days after transfection. Supernatants were cleared and concentrated through a 20% sucrose cushion. Cell and virion lysates were analyzed by Western blotting. Of note, human A3A is 3× HA tagged and is therefore larger than the 1× HA tagged macaque A3A. Tubulin serves as a loading control.