Fig 2.
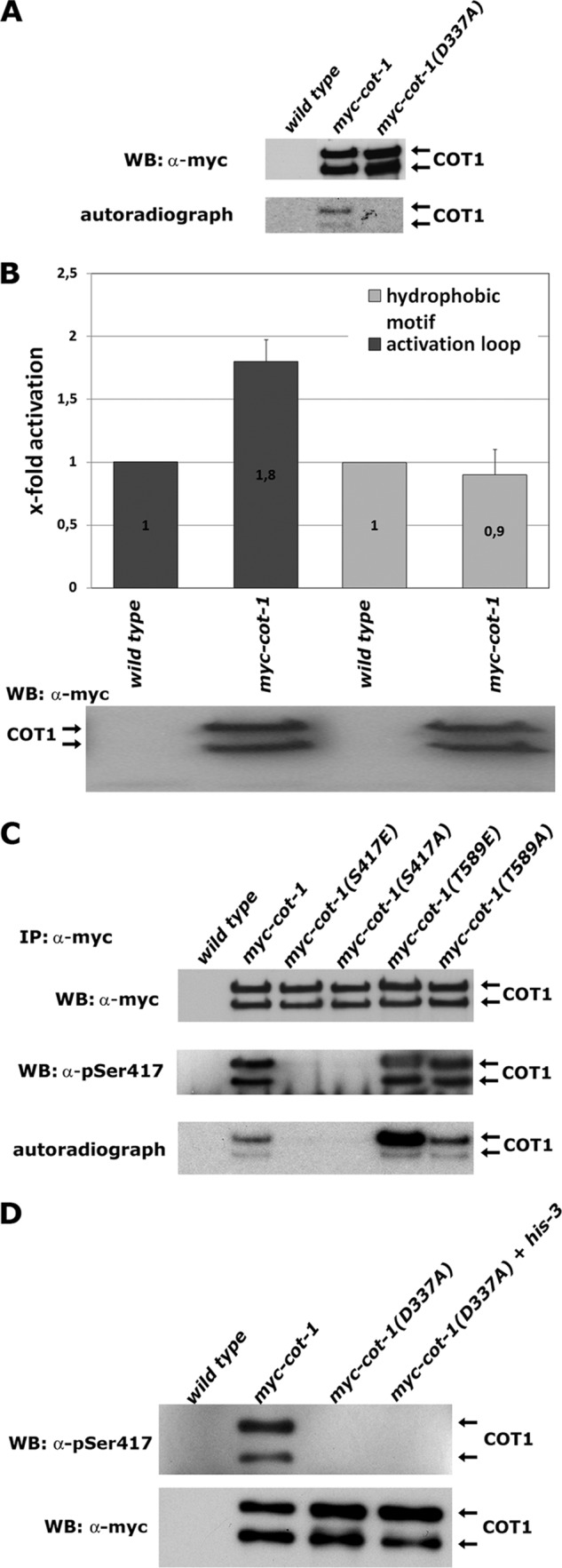
Ser417 is the only site of COT1 autophosphorylation. (A) Immunoprecipitated myc-COT1 variants from the indicated strains were probed with anti-myc antibody (upper panel) to determine equal amounts of precipitated kinase and subjected to a 32P in vitro autophosphorylation reaction (lower panel). WB, Western blotting. (B) In vitro kinase assays (performed in triplicate) with peptides covering the sequence of the activation segment (RSRRLMAYSTVGTPDYI) and hydrophobic motif (EESPELSLPFIGYTFKRFDNNFR) of COT1 as artificial substrates. Equal amounts of precipitated myc-COT1 used in the kinase reactions are shown below the graph. Phosphorylated amino acids are underlined. (C) Immunoprecipitated myc-COT1 variants from strains with the indicated genotypes were probed with anti-myc antibody (upper panel) or P-Ser417-specific antibody (middle panel) and subjected to an in vitro autophosphorylation reaction (lower panel). (D) Kinase-dead myc-COT1(D337A) was precipitated from a forced heterokaryon harboring an untagged copy of cot-1 and probed for Ser417 autophosphorylation in cis or in trans of the COT1 dimer with a phospho-Ser417-specific antibody (upper panel) or with an anti-myc antibody as a loading control (lower panel). The lack of myc-COT1(D337) phosphorylation purified from the heterokaryon indicates autophosphorylation of COT1 in cis.
