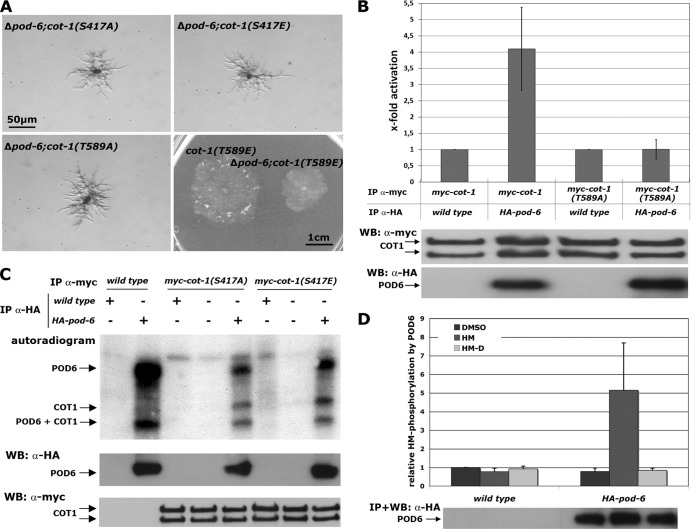
Fig 3.
COT1 is phosphorylated by the GC kinase POD6 in the hydrophobic motif. (A) Suppression analysis of Δpod-6 in strains expressing the indicated phospho variants of COT1. Note the partial suppression of Δpod-6 by myc-cot-1(T589E). (B) myc-COT1 purified from either the myc-cot-1 or the myc-cot-1(T589A) strain was preincubated with independently HA-precipitated HA-POD6 or mock precipitate from the wild type prior to a COT1 activity assay (five replicates) using the peptide KKRNRRLSVA as the substrate. COT1, but not COT1(T589A), activity was stimulated by POD6. Equal precipitation of myc-COT1 and HA-POD6 used in these assays was confirmed by Western blot (WB) analysis. (C) Direct phosphorylation of COT1 by POD6. Anti-HA precipitates from the HA-pod-6 or a mock control were mixed with precipitated myc-COT1(S417A), myc-COT1(S417E), or control precipitate. Autophosphorylation of HA-POD6 and POD6-dependent phosphorylation of myc-COT1 are indicated. The results shown in the middle and lower panels confirm that equal amounts of precipitated kinases COT1 and POD6 were used for these assays. (D) POD6 phosphorylates COT1 at Thr589 in the hydrophobic motif. Purified HA-POD6 and a control precipitate from the wild type were used for peptide-based in vitro kinase assays. Two peptides covering the hydrophobic motif (amino acids 576 to 589) of COT1 that carried either the wild-type sequence of COT1 or a Thr589-to-aspartate substitution (termed HM and HM-D, respectively) were used as artificial POD6 substrates (experiment performed in triplicate). DMSO was used as the solvent control, and the result obtained with this control was set as 1. An immunoblot of precipitated POD6 probed with anti-HA antibody showing equal amounts of purified kinase is presented below the graph.