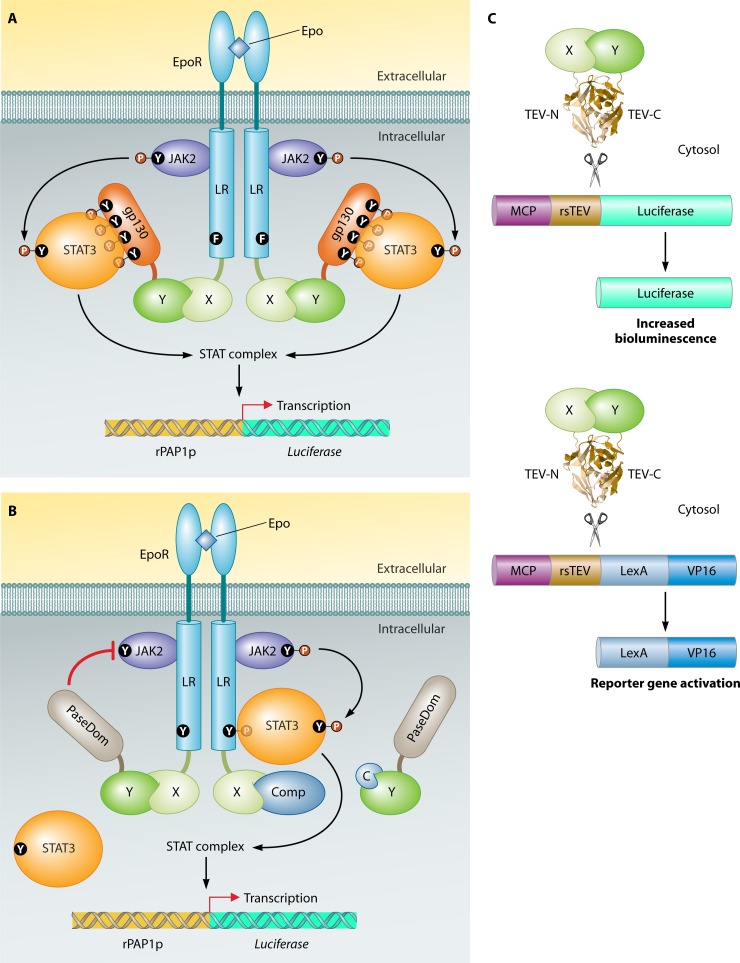
Fig 14.
Unique mammalian genetic PPI methods. (A) Mammalian protein-protein interaction trap (MAPPIT) (172). The bait protein is a fusion with a leptin receptor (LR), which contains three Y-to-F mutations so it is unable to activate STATs spontaneously (one representative phenylalanine [F] is shown). The prey fusion contains a domain of gp130 which can recruit STATs. After interaction of the bait with the prey, Janus kinases (JAKs) phosphorylate gp130, which stimulates binding of gp130 with the STATs. The STATs themselves are phosphorylated by the JAKs, which results in the formation of a STAT complex. The STAT complex binds the rat PAP1 promoter (rPAP1p) and activates luciferase transcription. The leptin receptor is further fused with the extracellular domain of EpoR, a receptor of erythropoietin (Epo), and therefore LR complex formation, which is necessary to make the association with the JAKs, is induced by addition of Epo. (B) Reverse MAPPIT (171). For reverse MAPPIT, a functional LR protein is used with one tyrosine (Y) residue that can be phospharylated upon activation. (Left) The prey Y fusion contains a phosphatase (PaseDom) domain which, upon interaction with bait X, removes the phosphate of JAK2, thereby preventing STAT recruitment. (Right) Inhibition of the bait-prey association by competing proteins (Comp) or compounds (C) reestablishes normal JAK-STAT signaling, which ultimately leads to luciferase reporter gene transcription. (C) Split-TEV method (698). Bait protein X and prey protein Y are fused to the N-terminal and C-terminal domains, respectively, of TEV protease. Association of X with Y initiates the reconstitution of a fully functional TEV protease, which cleaves TEV-specific recognition sequences (rsTEV). A membrane-bound or cytoplasmic protein (MCP), linked by an rsTEV to either luciferase or the artificial transcription factor LexA-VP16, prevents strong bioluminescence or LexA-VP16 nuclear localization, respectively. TEV protease activity releases luciferase, for induction of strong luminescence, or LexA-VP16, for reporter gene activation. The image of TEV protease is based on the PDB structure under accession number 1LVM (512).