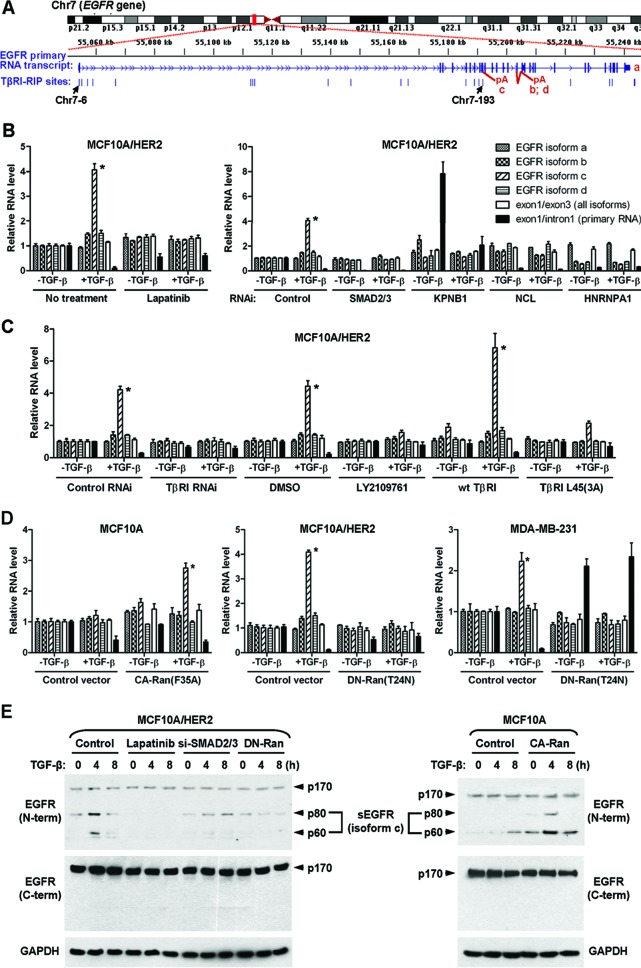
Fig 6.
Nuclear TβRI selectively induces EGFR splicing isoform c. (A) Schematic of the human EGFR gene and the positions of all identified TβRI-binding RNA sites that were aligned to the EGFR gene. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR of various EGFR-derived RNAs in MCF10A/HER2 cells treated or transfected as indicated. Data were normalized to the level of GAPDH and then compared to that in untreated cells (the first set of bars). Each data point represents the mean ± standard deviation of 3 wells. *, P < 0.001. Abbreviations are the same as in Fig. 2. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR of EGFR-derived RNAs in MCF10A/HER2 cells treated or transfected as indicated. *, P < 0.001. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide. (D) Quantitative RT-PCR of EGFR-derived RNAs in cells transfected with various Ran constructs. *, P < 0.001. (E) MCF10A and MCF10A/HER2 cells were treated or transfected as indicated before whole-cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting for detection of various EGFR isoforms. The positions of 60- and 80-kDa sEGFR generated from the splicing isoform c are indicated.