Figure 8. Analysis of PknBSA-KD crystal contacts.
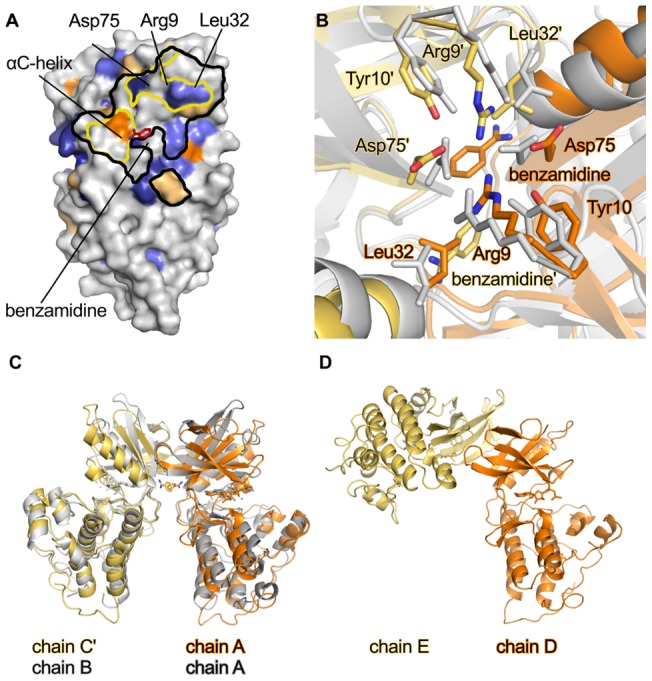
(A). Footprint of contacts between a symmetry mate of molecule C (C′) and molecule A in the crystals. Molecule A is shown in surface representation. Areas within black lines indicate crystal contacts with molecule C′ (distance <4.5 Å). Areas within yellow lines indicate the residues involved in dimer formation [22]. The surface conservation is shown as in Fig. 7, and the benzamidine is bound to chain A of PknBSA-KD is shown as a red stick model. Molecule pairs B/B′ and C′/A form similar crystal contacts. (B). Detailed view into the dimer interface formed by the A/C′ dimer. Chains A and C′ of PknBSA-KD are shown in orange and yellow, respectively. Chains A and B of dimeric M. tuberculosis PknB (PDB ID: 1MRU [24]) are in grey. Residues Arg9, Tyr10, Leu32 and Asp75, which are involved in dimer formation, are represented with sticks. These residues were also used for superimposing the two dimers. (C). Overview of the orientation of the dimer of M. tuberculosis PknB and PknBSA-KD. The colors are the same as in panel B. The N-lobes of PknBSA-KD chain A and M. tuberculosis PknB chain A were superposed. (D). Crystal contact involving chains D and E in PknBSA-KD. The orientation of chain D is the same as that of chain A in panel C.
