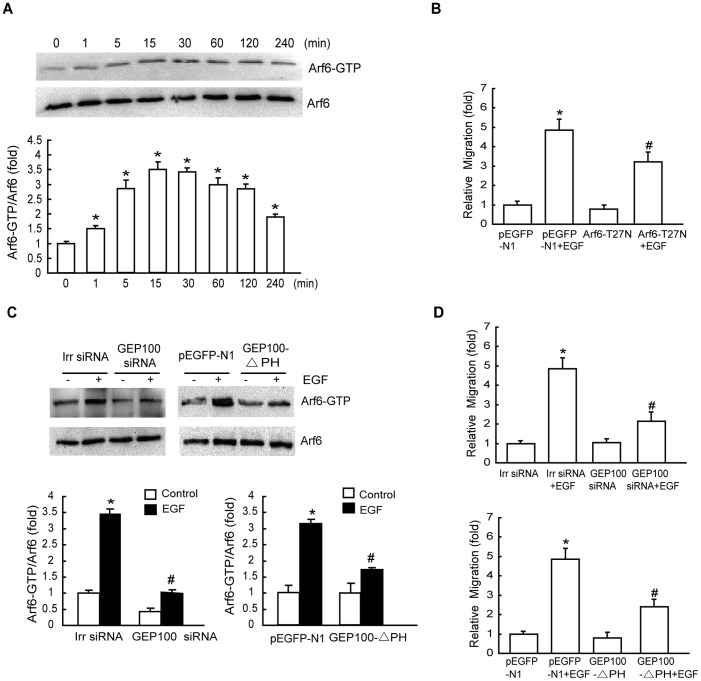
Figure 2. Effects of GEP100/Arf6 on EGF-induced cell migration.
(A) EGF induces activation of Arf6. Serum-starved cell monolayers were treated with 10 ng/mL EGF for the indicated times. Cellular lysates were assayed for active Arf6 by pulldown assays as described in ‘Materials and methods’. The data were mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (B) Effect of the inactive mutant of Arf6 on EGF-stimulated migration. HepG2 cells were transiently transfected with the empty vector pEGFP-N1 and Arf6-T27N, respectively. Cells were then subjected to a Transwell migration assay in the presence of 10 ng/mL EGF for 8 h. (C) Both GEP100-siRNA and GEP100-△PH transfection inhibit Arf6 activation. Cells transfected with GEP100-siRNA or GEP100-△PH were stimulated with EGF for 15 min, and Arf6-GTP levels were examined. (D) Effects of the GEP100-siRNA and GEP100-△PH on EGF-stimulated cell migration. HepG2 cells infected with GEP100-siRNA and GEP100-△PH as indicated were subjected to a Transwell migration assay in the presence of 10 ng/mL EGF for 8 h. *: P<0.05, referring to the difference between cells treated with and without EGF. #: P<0.05 (t-test), referring to the difference between the cells transfected with Arf6–T27N or GEP100 siRNA or GEP100-△PH plus EGF and the cells transfected with scrambled siRNA (irr siRNA) or empty vector plus EGF.