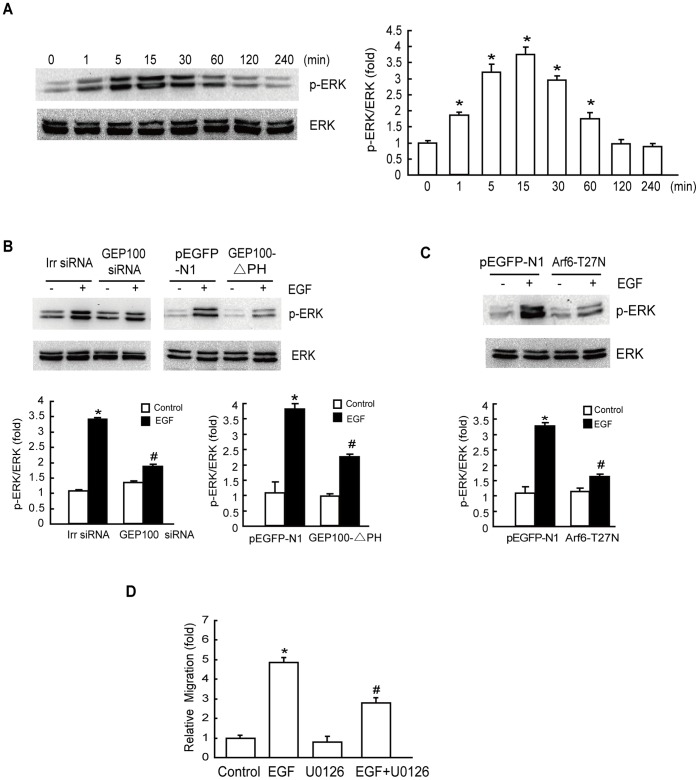
Figure 3. EGF activates ERK via the GEP100/Arf6 pathway that is required for EGF-induced cell migration.
(A) Effect of EGF on the activation of ERK. HepG2 cells were starved overnight, followed by treatment with 10 ng/mL EGF for the indicated times. Phosphorylation of ERK at Thr202/Tyr204 was determined as described in ‘Materials and methods’. (B) Both GEP100-siRNA and GEP100-△PH transfection inhibit ERK activation. Cells transfected with GEP100-siRNA or GEP100-△PH were stimulated with EGF for 15 min, and the activation of ERK was examined. (C) EGF-activated ERK depends on Arf6. HepG2 cells were transiently transfected with the empty plasmid pEGFP-N1 and Arf6-T27N, respectively. The cells were then treated with or without EGF (10 ng/mL) for 15 min after an overnight serum starvation and ERK activity was examined. (D) Effect of ERK inhibitor on EGF-stimulated cell migration. After pretreatment with 10 µM U0126 for 60 min, HepG2 cells were incubated with 10 ng/mL EGF for 8 h and the cell migration rate was determined by Transwell migration assay. *: P<0.05, referring to the difference between cells treated with and those without EGF. #: P<0.05 (t-test), referring to the difference between the cells transfected with Arf6–T27N or GEP100 siRNA or GEP100-△PH plus EGF and the cells transfected with scrambled siRNA (irr siRNA) or empty vector plus EGF.