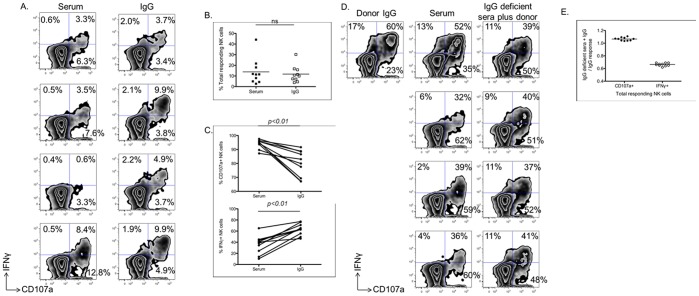
Figure 2. Effect of IgG purification on NK cell-mediated ADCC.
The impact of non-IgG soluble sera factors was assessed by activating NK cells for ADCC functionality in the presence of whole sera, purified IgG, or common purified IgG in the presence of IgG-depleted sera from a series of donors. (A) Zebra plots depict the anti-HIV ADCC mediated by NK cells when incubated with whole sera or IgG purified from the same sera. The values depicted represent the percentages of total NK cells mediating CD107a+IFNγ−, CD107a−IFNγ+, or CD107a+IFNγ+ functional profiles. (B) The scatter plot depicts a comparison of the percentage of total NK cells mediating ADCC-induced effector functions after stimulation of NK cells from a common donor with sera or IgG purified from sera. This difference was assessed with a paired T-test. (C) The graph on the top illustrates the percent of responding NK cells expressing CD107a after stimulation with sera or IgG purified from the same sera. The graph on the bottom illustrates the percent of responding NK cells producing IFNγ after stimulation with sera or IgG purified from the same sera. Differences were assessed with paired T-tests. (D) Zebra plots depict the response of NK cells from a common donor to anti-HIV ADCC when incubated with purified IgG from a common donor, sera from a series of donors, or purified IgG from a common donor combined with IgG-depleted sera from the series of donors. The values depicted represent the percentages of responding NK cells mediating CD107a+IFNγ−, CD107a−IFNγ+, or CD107a+IFNγ+ functional profiles. (E) The graph illustrates the alteration of the NK cell-mediated ADCC functional profile induce by the common purified IgG after the addition of IgG-depleted sera from a series of donors.