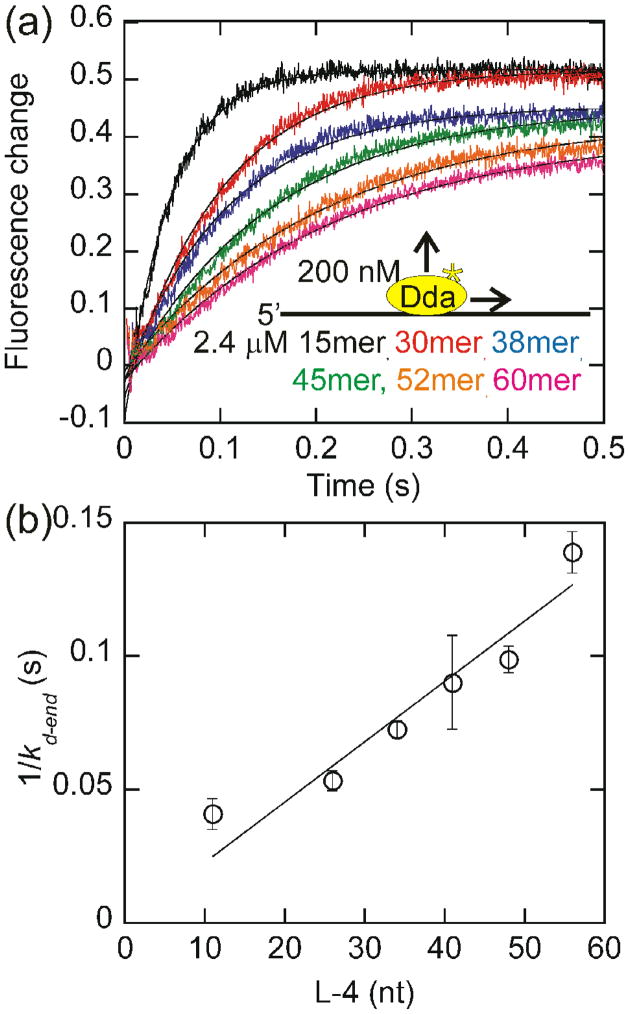
Fig. 3.
Measurement of the rate of dissociation of Dda from oligonucleotides of increasing length. (a) The change in fluorescence of Dda (200 nM) as it dissociates from 2.4 μM oligonucleotide of increasing length in the presence of ATP is plotted. The rate constants obtained from single exponential fits were 26.3 ± 1.1 s−1, 22.6 ± 1.8 s−1, 16.4 ± 0.8 s−1, 13.6 ± 2.8 s−1, 12.1 ± 0.6 s−1, and 8.7 ± 0.4 s−1 for dissociation from the 15mer, 30mer, 38mer, 45mer, 52mer, and 60mer, respectively. (b) The inverse of the rate constant for dissociation from the end of the oligonucleotide, kd-end is plotted versus the length of the substrate, adjusted for binding site size. Only oligonucleotides of at least 30 nucleotides in length are included in the fit. One-half the inverse slope of the resulting line provides a rate of translocation by Dda of 252 ± 11 nucleotides/s. The fit was constrained through the origin to constrain kd-in to the value measured in Fig. 2b.