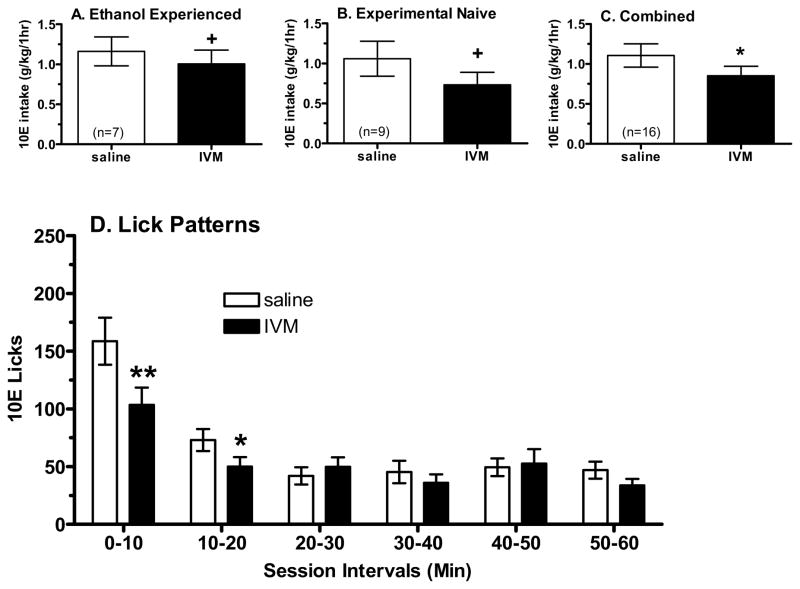
Figure 9.
Effect of IVM on operant self-administration of 10% ethanol (10E) in male C57BL/6J mice during 60 minute sessions. IVM tended to decrease 10E intake in animals with a long history of ethanol self-administration (panel A) or in animals that were experimentally naïve (panel B). Importantly, the data from the two cohorts did not differ, so the combined data indicated that IVM significantly decreased 10E intake (panel C). Panel D depicts the effect of IVM injection on the temporal distribution of 10E licks in 10 min intervals across the 60 min session in the combined data from the two cohorts (n=16). Values represent the mean ± SEM for the numbers of animals in parentheses for panels A–C. +p ≤ 0.10, *p < 0.05 versus saline (0 mg/kg), paired t-test.