Figure 2.
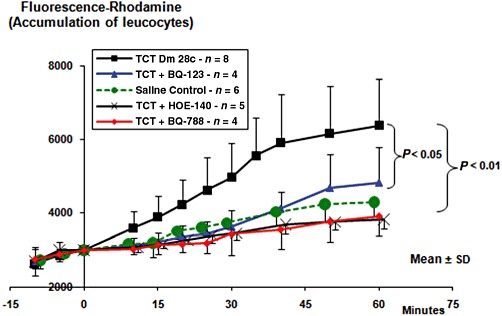
Intravital microscopy reveals the accumulation of rhodamine-labelled leucocytes in the hamster cheek pouch microcirculation. After labelling the leucocytes with i.v. injection of rhodamine, the superfusion of the cheek pouch was interrupted. After removing the superfusate, we applied 500 µL of BQ-123 (10 µM), or BQ-788 (10 µM) or the corresponding drug vehicle. In a separate group of hamsters, HOE-140 (0.5 µM) was added directly to the superfusion solution. Four minutes later, TCTs (3.107) or saline control were applied topically to the cheek pouch, and the incubation was prolonged up to 9 min total time. Controls (not shown) for drug vehicle were done by adding saline or saline-DMSO (0.4%) to the pouch for 4 min, prior to the application of TCTs. Results represent the mean ± SD of rhodamine fluorescence units in a 5 mm2 area of the cheek pouch. The results are representative of five series of experiments (n = 4–8 hamsters per group). P < 0.05; P < 0.01, as indicated).
