Figure 7.
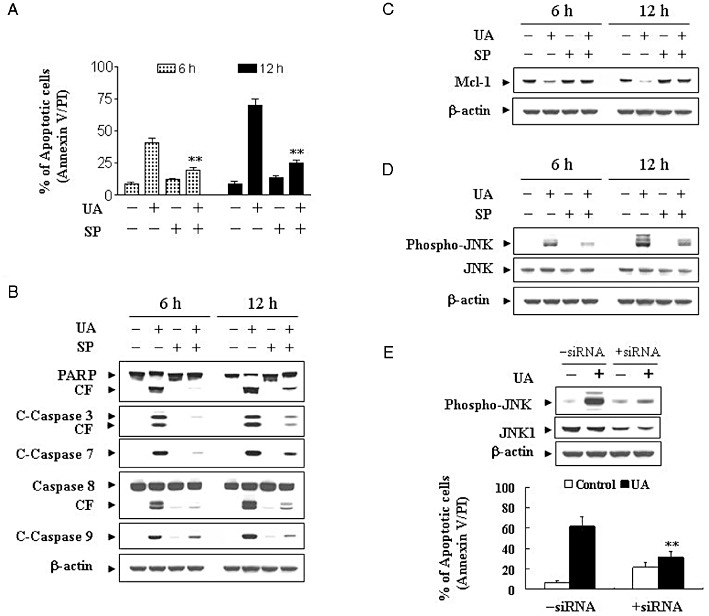
Pharmacological inhibition of JNK and transfection of JNK1 siRNA significantly protect cells from UA-induced apoptosis. U937cells were pretreated with 10 µM of the JNK inhibitor, SP600125 (SP), for 1 h, followed by the addition of 20 µM of UA for 12 h. (A) Cells were stained with Annexin V/PI, and apoptosis was determined using flow cytometry as described in Methods. The values obtained from Annexin V/PI assays represent the means ± SD for three separate experiments. **Values for cells treated with UA and SP were significantly less than those obtained for cells treated with UA alone by Student's t-test; P < 0.01. After treatment, total cellular extracts were prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis using antibodies against PARP, C-Caspase-3, C-Caspase-7, caspase-8 and C-Caspase-9 (B), Mcl-1 (C), as well as cell signalling proteins including phospho-JNK and JNK (D). (E) U937 cells were transiently transfected with JNK1 siRNA oligonucleotides or controls and incubated for 24 h at 37°C, after which cells were treated with 20 µM of UA for 12 h. Total cellular extracts were prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis using antibodies against phospho-JNK and JNK1. Apoptosis was determined using the Annexin V–FITC assay as described in Methods. **Values for cells treated with UA after transfection with JNK1 siRNA oligonucleotides were significantly decreased compared to those for control cells treated with UA by Student's t-test; P < 0.01.
