Figure 1.
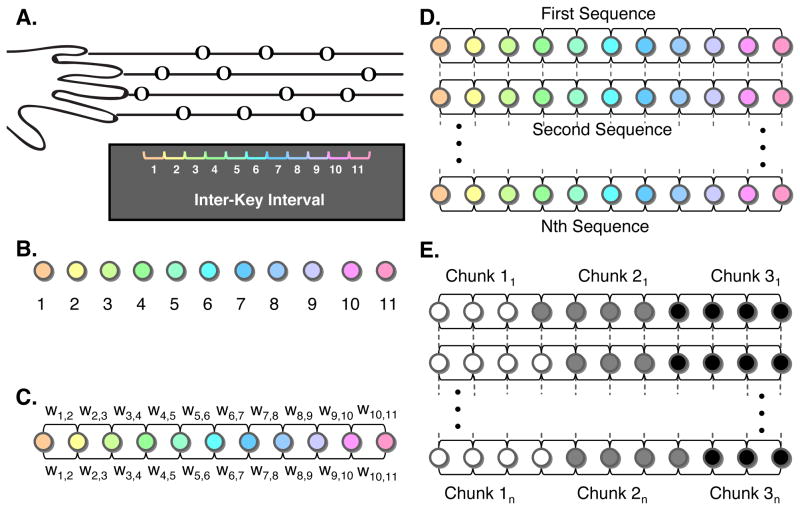
(A) A trial started with the onset of a static image depicting a sequence of 12 notes arranged in the style of sheet music. Presentation served as the signal to report the sequence of notes, which were read left to right proceeding one note to the next. Subjects reported the sequences using their non-dominant left hand, with the leftmost finger corresponding to notes on the top line and the rightmost finger corresponding to notes on the bottom line. Construction of a trial-by-trial sequence network for multi-trial community detection: Using the inter-key interval (IKI) between button presses, we constructed single-trial sequence networks by converting each IKI into a node (B), which are linked to each other using undirected edges. The weight (C) of an edge is defined as the normalized absolute value of the difference between the 2 IKIs that it connects (see Experimental Procedures). We applied multi-trial community detection to these sequence networks, and incorporated information between consecutive trials by linking each node in one trial network to itself in contiguous trials (D). Utilizing information from linked nodes in consecutive trials, we partitioned IKIs into chunks using a multi-trial community detection (D) that grouped nodes that were strongly connected to one another.