Figure 1. The MIDO of Ytm1 Interacts with Rea1’s MIDAS In Vivo and In Vitro.
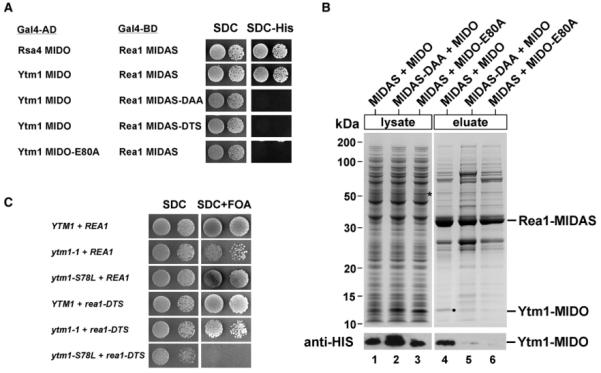
(A) Yeast two-hybrid interaction between wild-type and mutant alleles of Rea1-MIDAS and Ytm1-MIDO. Yeast two-hybrid plasmids expressing the indicated GAL4-BD (GAL4 DNA-binding domain) and GAL4-AD (GAL4 activation domain) fusion proteins were transformed into the yeast reporter strain PJ69-4A. Transformants were spotted in 10-fold serial dilutions onto SDC-Trp-Leu (SDC) or SDC-Trp-Leu-His (SDC-His) and incubated at 30 °C for 4 days. The Rea1-MIDAS comprises residues 4622–4910; the MIDO of Rsa4, residues 1–154; and the MIDO of Ytm1, residues 1–92. Growth on SDC-His plate indicates a two-hybrid interaction. (B) Rea1-MIDAS and Ytm1-MIDO bind directly to each other. The GST-TEV-tagged MIDAS of Rea1 (wild-type or DAA mutant; residues 4608–4910) was coexpressed with His6-Ytm1-MIDO (1–92 aa) or the His6-Ytm1-MIDO E80A mutant in E. coli in the indicated combinations. The GST-MIDAS fusion proteins were affinity purified on GSH beads and eluted by TEV cleavage. Supernatants and eluates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining (top) and western blotting (bottom) using anti-HIS antibodies to detect Ytm1 in eluates and total cell lysates. Protein bands above GST-MIDAS are E. coli contaminants. (C) The ytm1-MIDO mutant S78L is genetically linked to the rea1-DTS mutant. The YTM1Δ/REA1Δ double-shuffle strain was transformed with wild-type and the indicated mutant alleles of YTM1 and REA1, respectively. Transformants were spotted in 10-fold serial dilutions onto SDC-Trp-Leu (SDC) or SDC+FOA to test for synthetic lethality. Plates were incubated at 30 °C for 2 (SDC) or 4 days (SDC+FOA).
A sequence analysis of Ytm1 MIDO is shown in Figure S1.
