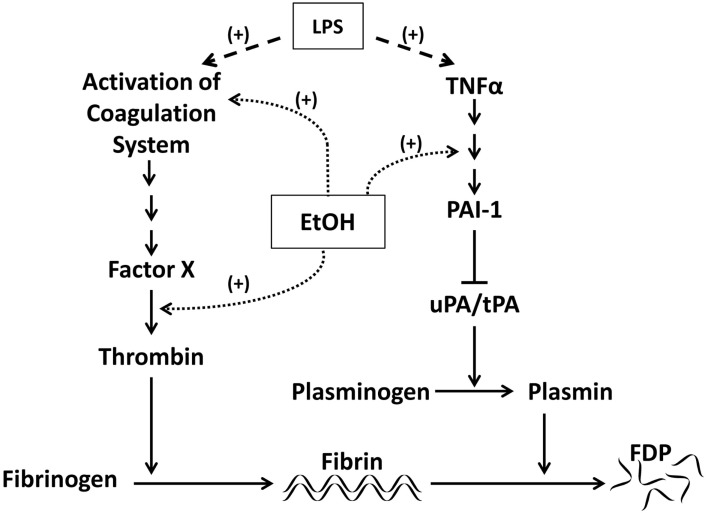
Figure 1.
Effects of LPS and ethanol on PAI-1 and fibrinolysis. Activation of the coagulation cascade by LPS via thrombin results in accumulation of cross-linked fibrin. Cross-linked fibrin is degraded by plasmin. PAI-1 blocks fibrinolysis by inhibiting the plasminogen activators uPA and tPA and therefore the activation of plasmin. Both ethanol and LPS can modulate signaling downstream of the coagulation cascade, increasing fibrin deposition. Ethanol may also blunt fibrin degradation by altering signaling downstream of TNFα. LPS can have similar effects on fibrinolysis by stimulating release of TNFα.