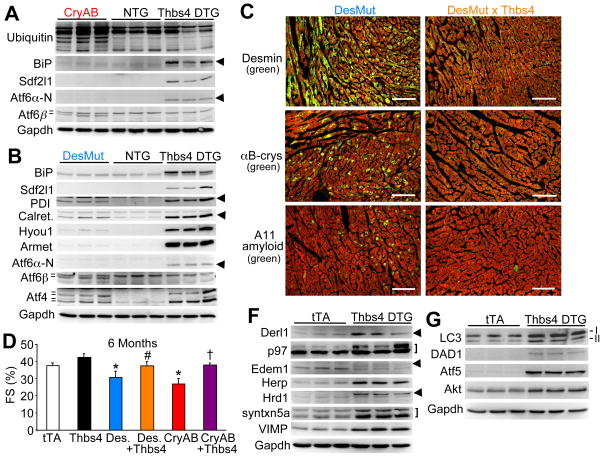
Figure 3.
Thbs4 induces a unique ER stress response signature that antagonizes protein aggregation and disease in the heart. (A) Western blots showing ER protein expression in αB-crystallin (CryAB) mutant or (B) desmin (DesMut) mutant hearts in comparison to non-transgenic (NTG) and Thbs4 DTG hearts. The hash marks or arrowheads show the different isoforms that were detected. (C) Immunohistochemistry of frozen heart sections from 6-month old mice of the indicated genotypes. Protein aggregation (green color) is dramatically reduced when Thbs4 is over-expressed. Red staining is for actin and shows the outline of cardiomyocytes (scale bars = 100 μm). (D) FS% as determined by echocardiography suggests that cardiac function is improved in both aggregation-prone cardiomyopathic transgenic mouse models when Thbs4 is overexpressed (N=6 or more mice in each group, *P<0.05 versus tTA; #P<0.05 versus DesMut; †P<0.05 versus CryAB). (F) Western blotting for proteins involved in ERAD from the hearts of Thbs4 DTG mice versus tTA control hearts. The arrowheads show the position of the relevant proteins, while the bracket shows 2 relevant bands. (G) Western blotting for proteins involved in autophagy (LC3, both I and II isoforms) or cellular protection. Also see Figure S5.