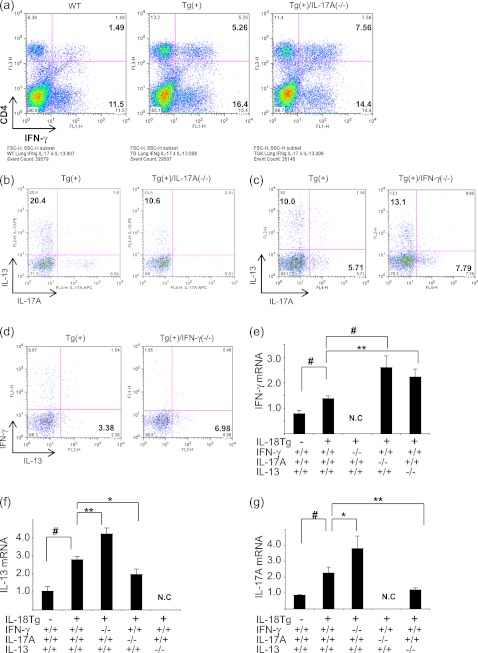
Figure 4.
Interactions between IFN-γ, IL-17A, and IL-13 in IL-18 transgenic (Tg) mice. Wild-type (WT) (Tg−) and IL-18 Tg (Tg+) mice with WT (+/+) and null (−/−) genetic loci were on doxycycline (Dox) water for 4 months. Lung parenchymal cells were isolated and accumulation of CD4+ cells that produce IFN-γ (a) and IL-13 (b) in the presence (+/+) or absence (−/−) of IL-17A was evaluated. The accumulation of CD4+ IL-17A–producing cells (c) and IL-13–producing cells (d) was evaluated in the presence (+/+) or absence (−/−) of IFN-γ. The levels of mRNA encoding IFN-γ (e), IL-13 (f), and IL-17A (g) mRNAs were also evaluated. b–d were evaluated after the CD4+ lymphocyte population was gated. The values in e–g represent the mean ± SEM of evaluations in a minimum of eight mice. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, # P < 0.001. N.C = not checked. a–d are representative of a minimum of three similar experiments.