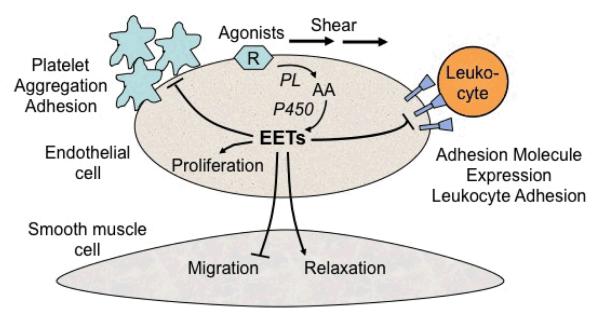
Figure 4.
A simplifed schematic of vascular effects of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs). Arrows denote stimulation, straight line without arrow denotes inhibition. Agonists or shear stress activate phospholipase (PL) in endothelial cell membranes. This releases arachidonic acid (AA) which is metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP) to EETs. EETs can diffuse to the vascular smooth muscle cell to cause relaxation and inhibit cell migration. EETs inhibit adhesion molecule expression on endothelial cells which decreases leukocyte adherence. EETs prevent platelet aggregation and adhesion. EETs promote angiogenesis by stimulating endothelial cell proliferation.