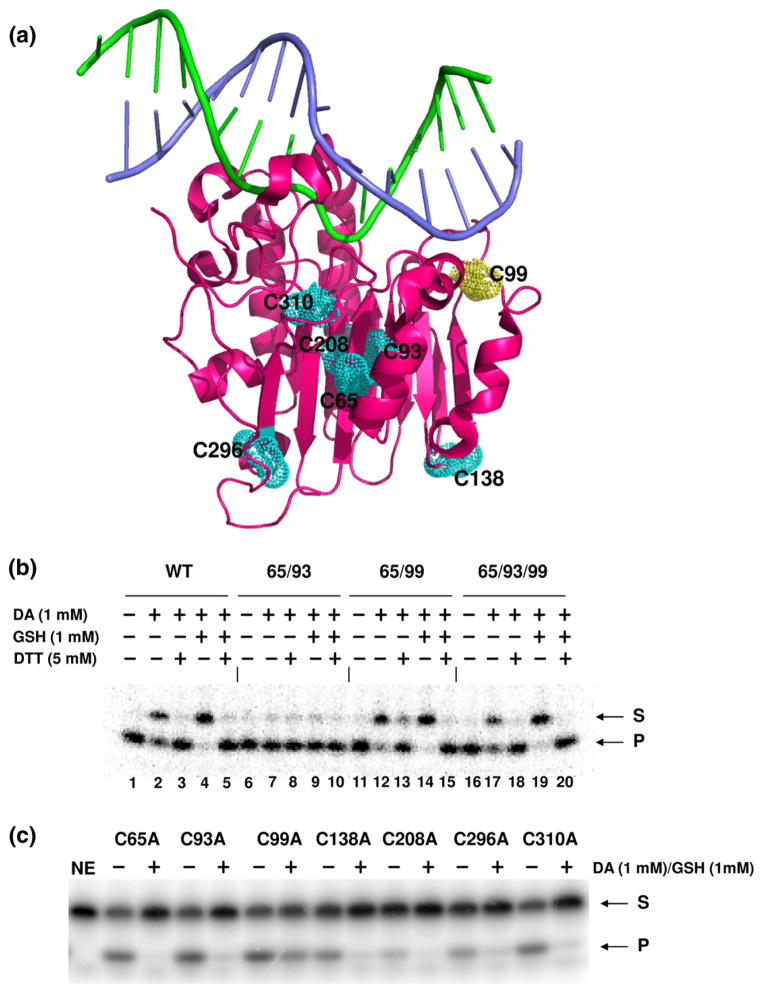
Fig. 4.
Identification of S-glutathionylated cysteine residue in APE1. (a) The three-dimensional structure of the human APE1 protein is shown as a magenta ribbon rendering with the seven cysteine residues depicted as van der Waals spheres. Substrate DNA is shown as a stick rendering with the abasic site containing strand in green and the complementary strand in purple. The rendering was generated from coordinate file 1DEW (Protein Data Bank accession number) by using the PyMOL Molecular Graphics System (Version 1.3, Schrödinger, LLC). Inhibitory effect of S-glutathionylation on AP endonuclease activity was measured using APE1 proteins retaining all seven cysteine residues (WT) or two or three of the N-terminal cysteine residues (Cys65, Cys93, and Cys99). The other cysteine residues not designated are substituted with Ala. Treatment parameters are indicated, and S=substrate and P=product. The data are representative of at least three independent experiments. APE1 cysteine mutants were generated by a single amino acid substitution (to Ala) and tested for AP endonuclease activity. Each cysteine mutant protein was treated with 1 mM diamide plus 1 mM GSH where indicated (+). The data are representative of at least three independent experiments.